Overview
Itchy skin, also known as pruritus, is an uncomfortable sensation that creates an urge to scratch. It may affect a small area of the body or be widespread and can occur with or without visible skin changes. Pruritus can be temporary or chronic and may result from skin conditions, systemic diseases, or environmental factors. Persistent or severe itching can significantly impact sleep, daily activities, and overall quality of life.
Symptoms
The main symptom is itching, which may vary in intensity. Associated symptoms can include:
-
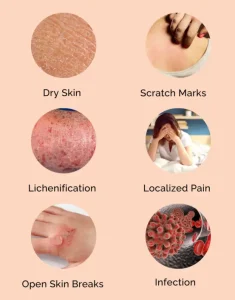
Dry, rough, or flaky skin
-
Redness or inflammation
-
Rash, bumps, or blisters depending on the cause
-
Thickened or scaly skin from repeated scratching
-
Burning or stinging sensation
-
Worsening itching at night
Causes
Itchy skin can result from a wide range of conditions affecting the skin or internal organs. Common causes include:
-
Dry skin, especially in older adults
-
Allergic reactions or contact dermatitis
-
Eczema, psoriasis, or hives
-
Insect bites or infestations
-
Liver or kidney disease
-
Thyroid disorders
-
Diabetes
-
Certain medications
Risk factors
-
Older age
-
Cold or dry climates
-
Frequent bathing with hot water
-
History of allergies or skin conditions
-
Chronic medical conditions affecting organs
-
Use of irritating soaps or skincare products
Complications
-
Skin infections due to broken skin from scratching
-
Thickened or scarred skin
-
Sleep disturbances
-
Anxiety or emotional distress
-
Reduced quality of life
Prevention
Itchy skin may be prevented or reduced by adopting skin-friendly habits, including:
-
Keeping skin well moisturized
-
Using mild, fragrance-free soaps and cleansers
-
Avoiding hot showers and long baths
-
Wearing loose, breathable clothing
-
Managing underlying medical conditions
-
Seeking medical evaluation for persistent or unexplained itching
Addressing the underlying cause of pruritus is key to effective treatment and long-term relief.
Advertisement