Overview
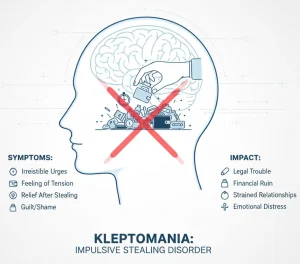
Kleptomania is a rare mental health disorder characterized by a recurring inability to resist the urge to steal items that are not needed for personal use or financial gain. The behavior is impulsive rather than planned and is often followed by feelings of guilt, shame, or distress. Kleptomania is classified as an impulse control disorder and is not the same as ordinary theft.
Symptoms
Symptoms of kleptomania are primarily behavioral and emotional, and they tend to recur over time.
Common symptoms include:
-
Repeated urges to steal items of little or no value
-
Rising tension or anxiety before stealing
-
Feelings of relief or gratification during the act
-
Guilt, shame, or remorse after stealing
-
Hiding, discarding, or giving away stolen items
-
Difficulty controlling impulses despite negative consequences
Causes
The exact cause of kleptomania is not fully understood. It is believed to result from a combination of psychological, biological, and neurological factors.
Possible causes include:
-
Imbalances in brain chemicals such as serotonin
-
Abnormalities in brain regions involved in impulse control
-
Coexisting mental health conditions such as anxiety or depression
-
Emotional stress or trauma
-
Genetic vulnerability in some individuals
Risk Factors
Certain factors may increase the risk of developing kleptomania.
Risk factors include:
-
History of mental health disorders
-
Family history of impulse control disorders
-
Substance use disorders
-
High levels of stress
-
Female sex, as the condition is diagnosed more often in women
Complications
If left untreated, kleptomania can lead to serious personal, legal, and social consequences.
Possible complications include:
-
Legal problems and criminal charges
-
Strained relationships with family and friends
-
Financial difficulties
-
Development of substance abuse
-
Depression, anxiety, or suicidal thoughts
-
Damage to self-esteem and quality of life
Prevention
There is no proven way to completely prevent kleptomania, but early recognition and treatment can reduce its impact and prevent complications.
Preventive strategies include:
-
Seeking mental health support for impulse-related behaviors
-
Managing stress through healthy coping mechanisms
-
Treating underlying mental health conditions promptly
-
Avoiding substance misuse
-
Encouraging awareness and education about impulse control disorders
If you want, I can also prepare sections on diagnosis, treatment options, or coping strategies in the same SEO-friendly, WordPress-ready format.
Advertisement