Diagnosis To determine whether you have thrombocytopenia, your healthcare professional will review your symptoms, medical history, and medications. The following tests and exams are commonly used: Blood test: A complete blood count measures the number of blood cells, including platelets, in a blood sample. Your healthcare professional may compare current results with past tests. Blood smear: A laboratory test examines …
Thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia (pronounced “THROM-bo-sigh-toe-PEE-ne-ah”) occurs when your bone marrow doesn’t make enough platelets. Platelets are blood cells that form blood clots to help stop bleeding. If you have thrombocytopenia, you may bleed a lot, and the bleeding may be hard to stop. Thrombocytopenia often affects people with certain medical conditions, like autoimmune disease or who take certain medications. Healthcare providers typically treat thrombocytopenia by treating the underlying …
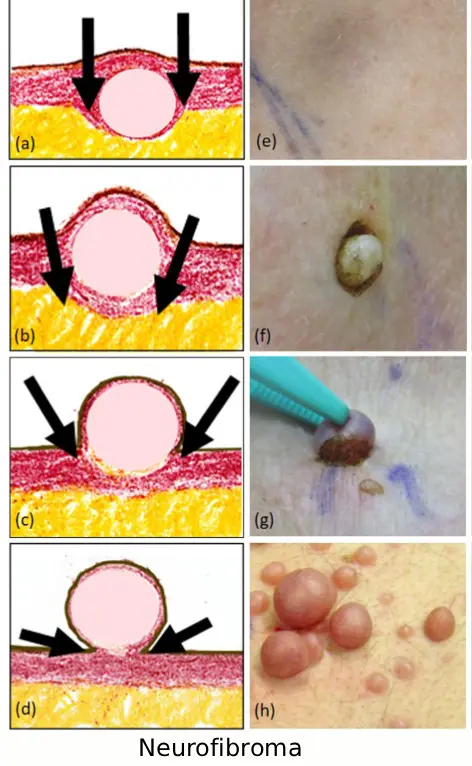
Neurofibroma
Diagnosis Diagnosis of a neurofibroma typically starts with a physical exam and a review of your medical history by a healthcare professional. Imaging tests may be performed to evaluate the tumor: CT scan or MRI to locate the tumor, detect very small tumors, and assess affected tissues PET scan to determine if the tumor is cancerous (malignant) or benign A …
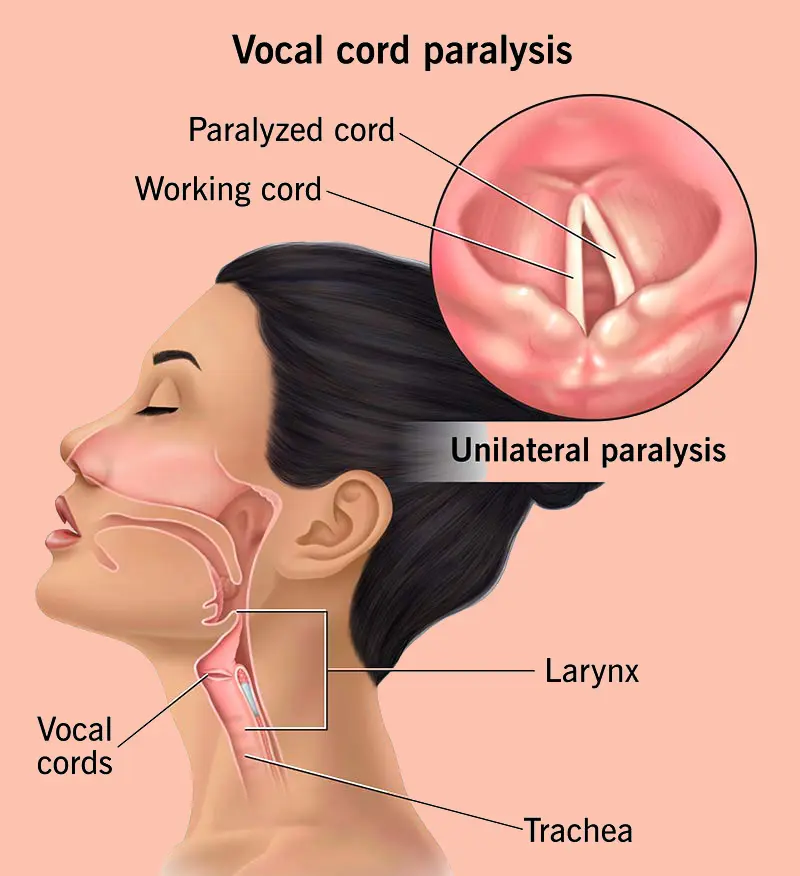
Vocal Cord Paralysis
Diagnosis To diagnose vocal cord paralysis, your healthcare professional begins by asking about your symptoms, voice changes, and lifestyle. A physical exam and voice evaluation help determine how long and how severely your voice has been affected. You may need several specialized tests, including: Laryngoscopy: This involves examining the vocal cords using a mirror or a thin, flexible tube called …
Yolk Sac Tumor
Diagnosis Diagnosing a yolk sac tumor involves a combination of physical exams, imaging tests, and laboratory studies. Since these tumors are rare and aggressive, early and accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment. Healthcare professionals typically begin with a physical examination and review of symptoms such as abdominal swelling, pain, or the presence of a lump in the testicles or …
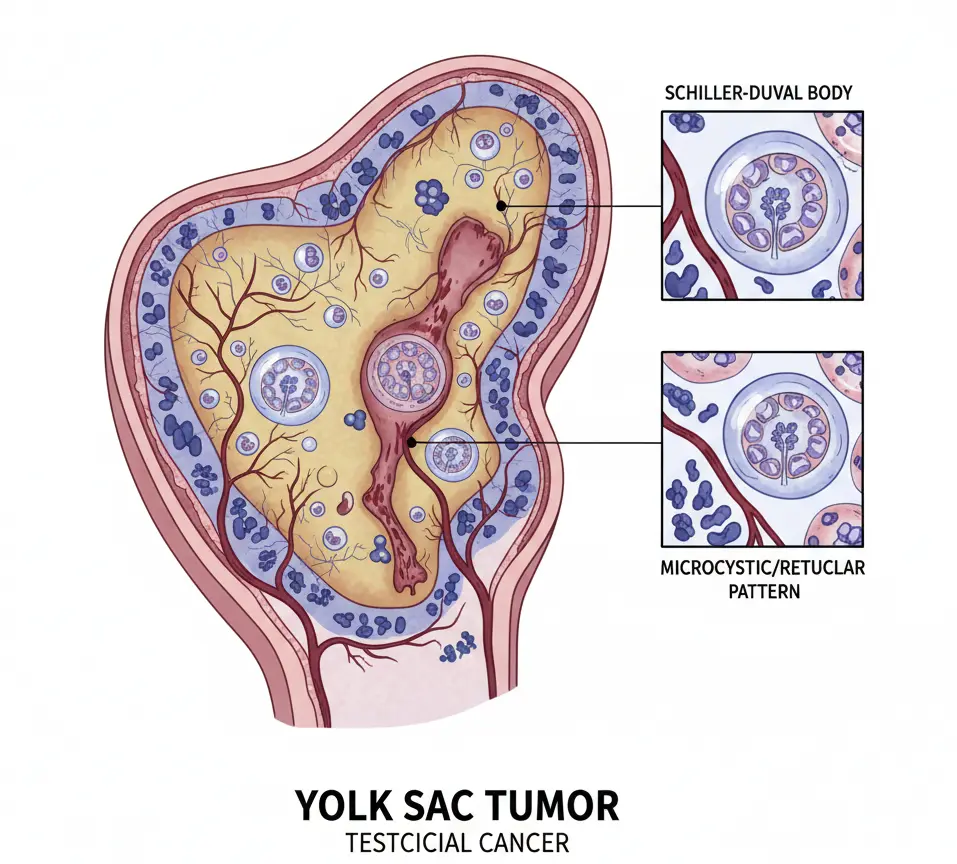
Yolk Sac Tumor
A yolk sac tumor is a rare and aggressive type of germ cell tumor that most often affects the ovaries or testes. It is also known as an endodermal sinus tumor. Yolk sac tumors are more common in children and young adults, but they can occur at any age. These tumors grow quickly and can spread if not treated promptly. …
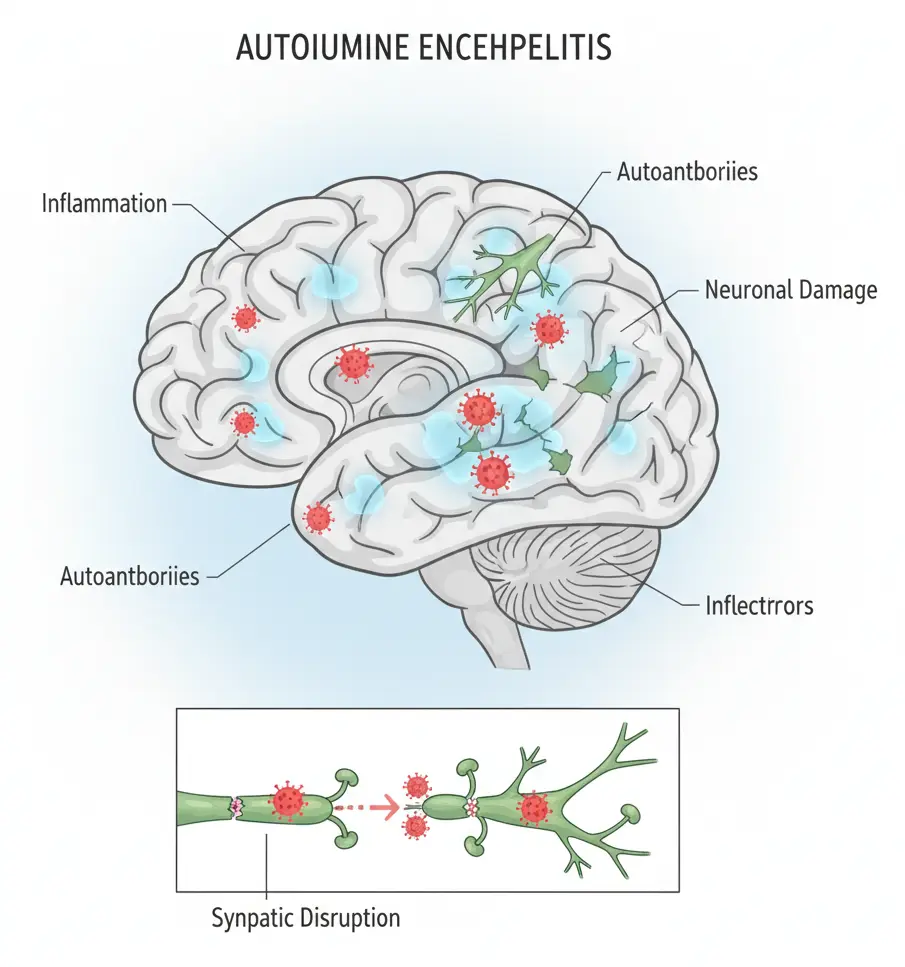
Autoimmune Encephalitis
Autoimmune encephalitis (AE) is a group of conditions that causes inflammation in the brain. This occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy brain cells. Symptoms can vary but often include memory loss, changes in thinking, changes in behavior, and seizures. Autoimmune encephalitis differs from infectious encephalitis, which is caused by viruses or bacteria and requires different treatments. Research suggests …
Autoimmune Encephalitis
Diagnosis Autoimmune encephalitis (AE) is a condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks the brain, causing inflammation and neurological symptoms. Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial, as AE can be misdiagnosed as other neurological or psychiatric conditions. Evaluation: A healthcare professional reviews your symptoms, medical history, and conducts a physical and neurological exam. Diagnostic Criteria: Specialists use AE criteria, looking …
Autoimmune Epilepsy
Diagnosis Autoimmune epilepsy is a type of epilepsy caused by the immune system attacking brain cells. Diagnosis begins with a physical exam and a detailed review of symptoms. Lab tests: Detect antibodies in the blood or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). CSF is collected via a lumbar puncture, where a needle removes fluid from the lower back for testing. Some people with …
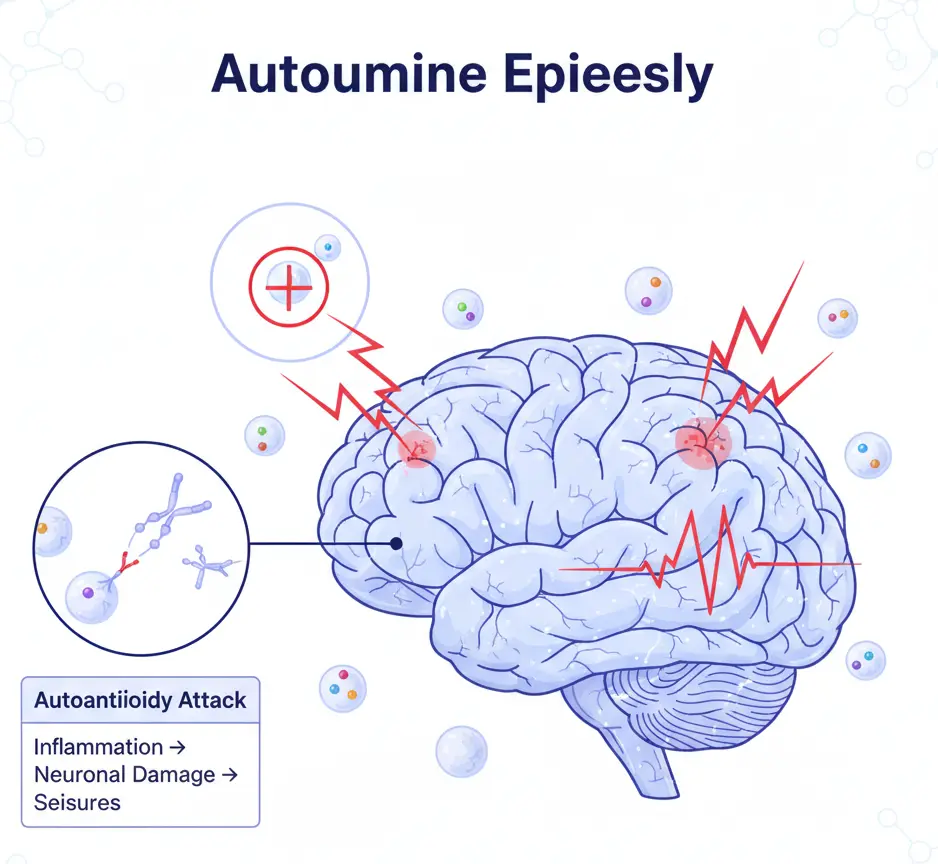
Autoimmune Epilepsy
Autoimmune epilepsy is a type of epilepsy in which seizures are caused by the immune system mistakenly attacking brain cells. It can occur alongside conditions affecting the immune system, particularly autoimmune encephalitis. This condition is also referred to as autoimmune associated epilepsy or acute symptomatic seizures secondary to autoimmune encephalitis. Antibodies, which usually protect the body from infections, target receptors …