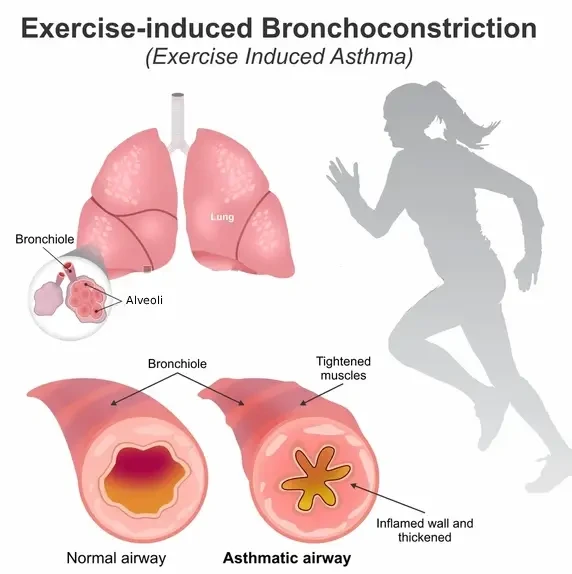
Exercise-induced asthma, also known as exercise-induced bronchoconstriction, is a condition in which physical activity triggers narrowing of the airways, making breathing difficult. It can occur in people with or without chronic asthma and is commonly triggered by vigorous exercise, especially in cold or dry air. Symptoms usually begin during exercise or shortly after stopping and can interfere with physical performance …
Occupational Asthma
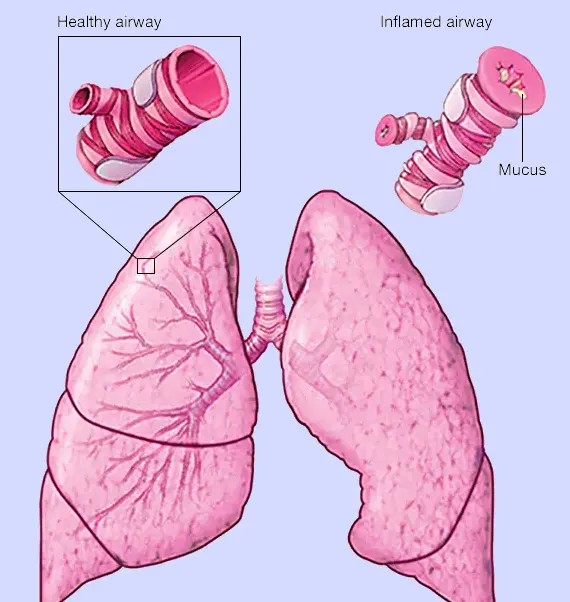
Occupational asthma is a type of asthma that is caused or worsened by exposure to substances in the workplace. It occurs when inhaling certain chemicals, dusts, fumes, or biological agents triggers airway inflammation and narrowing. Symptoms may improve away from work and worsen during working hours, making early recognition and intervention important to prevent long-term lung damage. Symptoms Symptoms of …
Astrocytoma
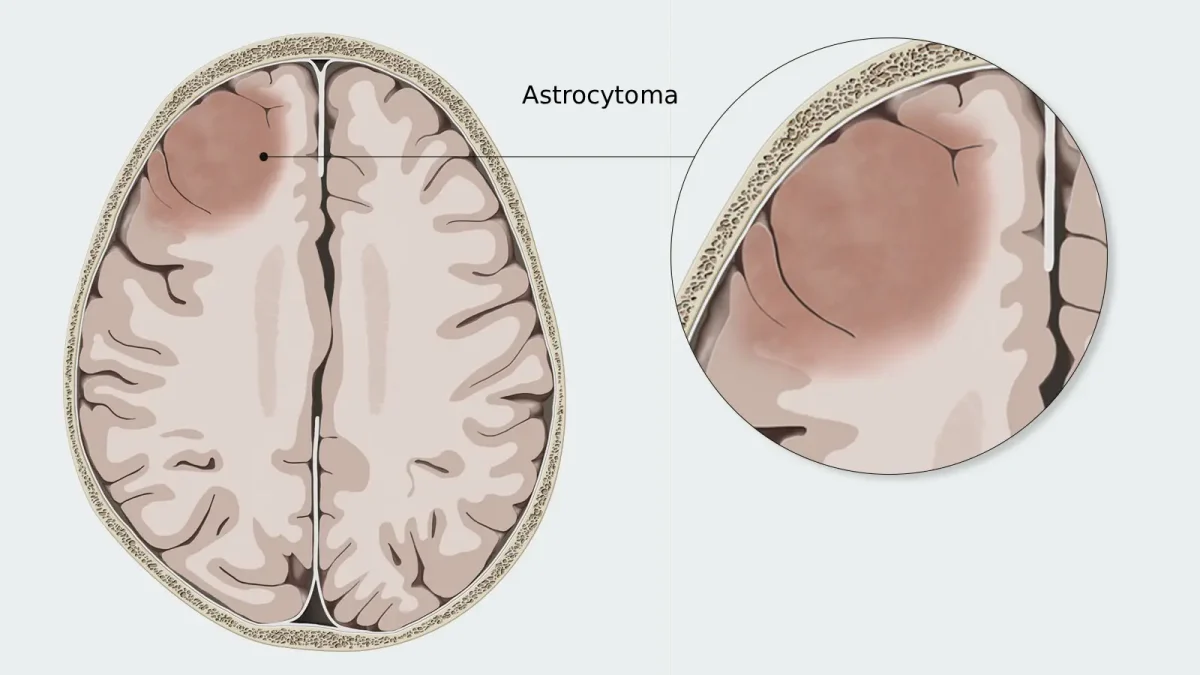
Astrocytoma is a type of brain tumor or spinal cord tumor that begins in astrocytes. Astrocytes are star-shaped cells that support nerve cells and help keep the brain and spinal cord functioning properly. Astrocytoma is part of a broader group of tumors called gliomas, which develop from glial cells that support and protect nerve cells. Astrocytomas can vary widely in …
Osteoarthritis
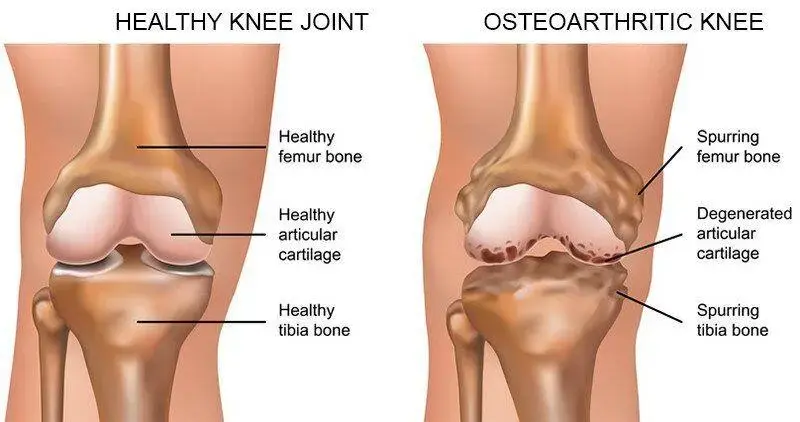
Osteoarthritis is a common, chronic joint disorder characterized by the gradual breakdown of cartilage that cushions the ends of bones. As the cartilage wears away, bones may rub against each other, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced joint mobility. Osteoarthritis most commonly affects weight-bearing joints such as the knees, hips, spine, and hands and tends to worsen over time. Symptoms …
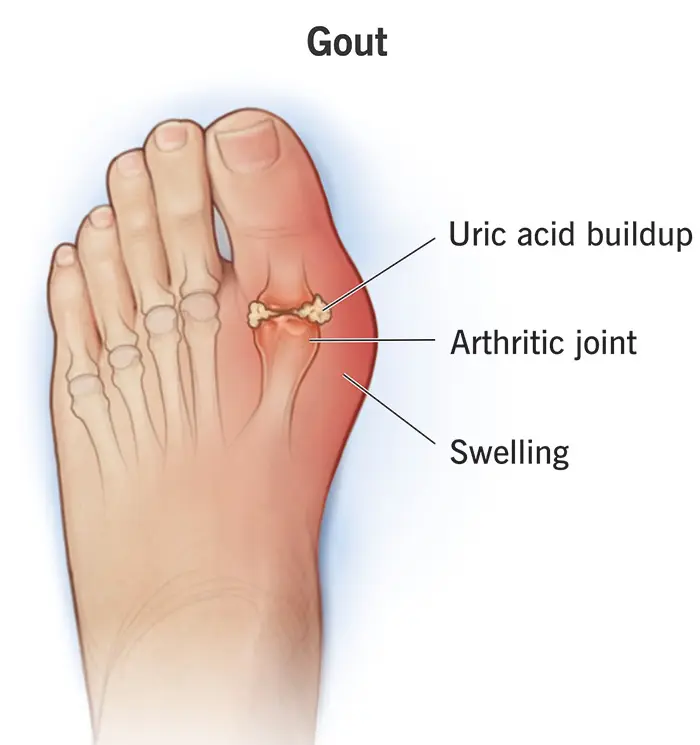
Gout
Gout is a type of inflammatory arthritis caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints. Uric acid forms when the body breaks down substances called purines, which are found naturally in the body and in certain foods. When uric acid levels become too high, crystals can accumulate in joints, leading to sudden and severe pain. Gout commonly …
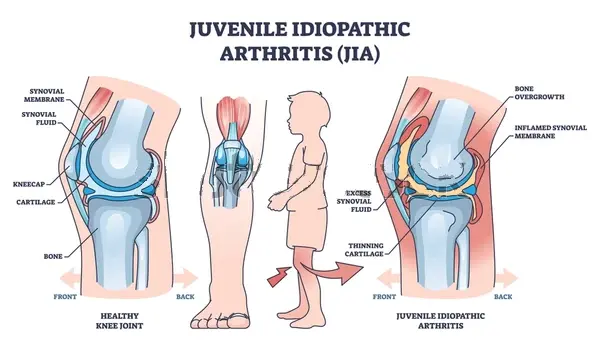
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
Juvenile idiopathic arthritis is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects children under the age of 16. It is characterized by persistent joint inflammation that lasts for at least six weeks and has no identifiable cause. The condition can involve one or multiple joints and may also affect other parts of the body, such as the eyes or internal organs. Juvenile …
Psoriatic Arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis is a type of arthritis. It usually affects people who have psoriasis or a biological family history of psoriasis. Arthritis is a common disorder that affects your joints. It causes pain and inflammation in and around your joints. Psoriasis causes inflammation in your skin. Psoriasis rashes are patches of discolored skin covered with scales. These thick, scaly areas are called plaques. …
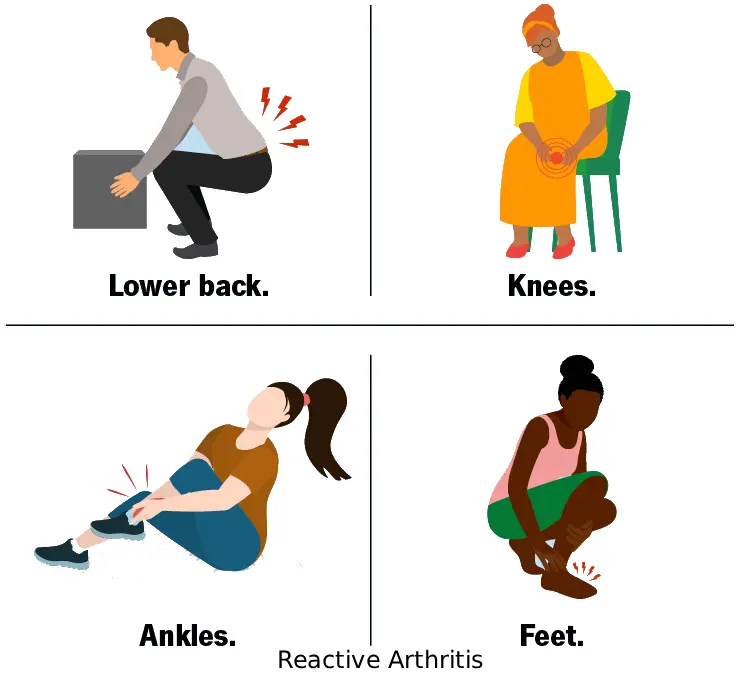
Reactive Arthritis
Reactive arthritis is an inflammatory joint condition that develops as a reaction to an infection in another part of the body, most commonly the gastrointestinal or genitourinary tract. The arthritis itself is not caused by direct infection of the joints but by an abnormal immune response triggered by the initial infection. Reactive arthritis often affects the knees, ankles, and feet …
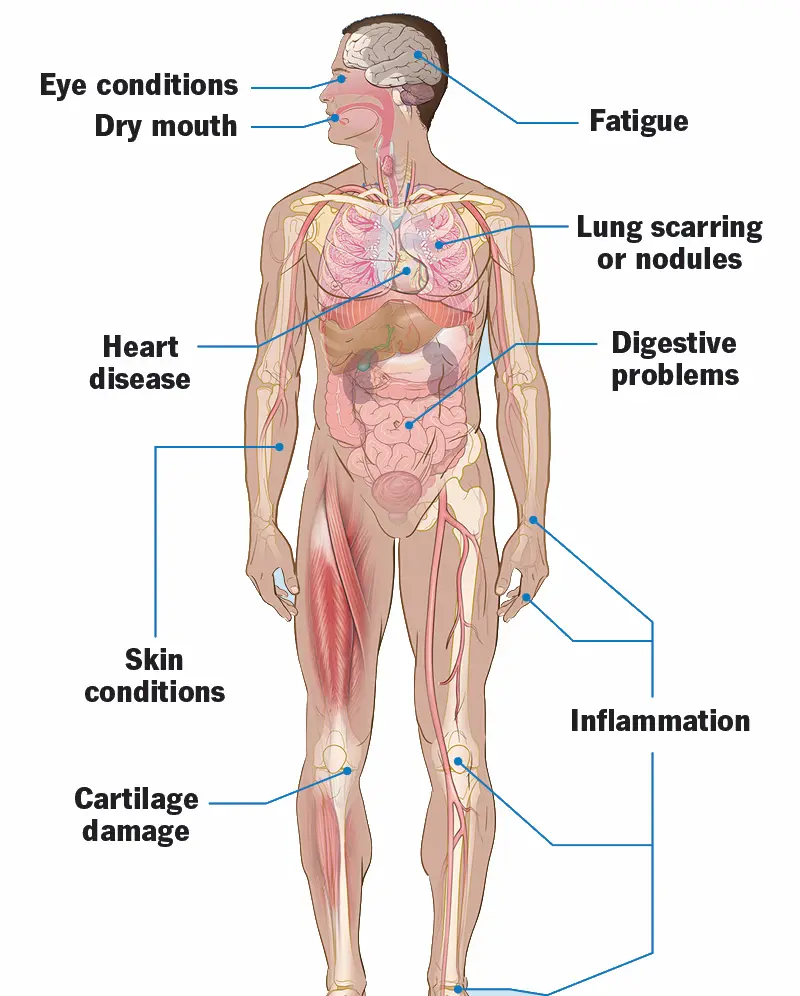
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the joints, causing inflammation, pain, and progressive joint damage. Unlike osteoarthritis, which results from wear and tear, rheumatoid arthritis occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the lining of the joints. The condition can affect people of all ages but is most common in middle-aged adults and tends to be …
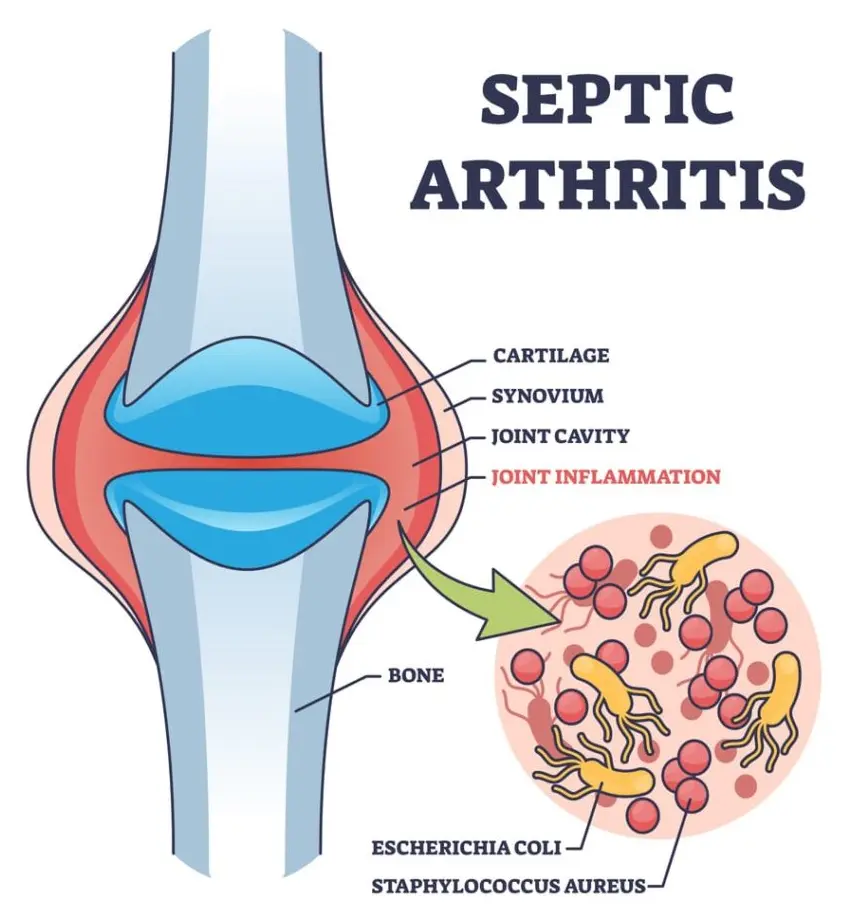
Septic Arthritis
Septic arthritis is a serious joint infection caused by microorganisms, most commonly bacteria. It leads to inflammation within a joint, resulting in pain, swelling, and reduced movement. The condition can develop rapidly and may cause permanent joint damage if not treated promptly. Septic arthritis can affect people of any age, but it is more common in older adults, young children, …