Overview
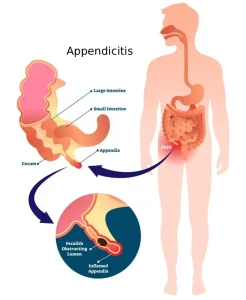
Appendicitis is an inflammation of the appendix. The appendix is a small, finger-shaped pouch attached to the colon on the lower right side of the abdomen.
Appendicitis commonly causes pain in the lower right abdomen. In many people, the pain starts near the belly button and then moves to the lower right side. As the inflammation worsens, the pain usually becomes more severe and persistent.
Anyone can develop appendicitis, but it most often occurs between the ages of 10 and 30. Treatment usually involves antibiotics and, in most cases, surgery to remove the appendix.
Symptoms
Symptoms of appendicitis can vary from person to person and may change as the condition progresses.
Common symptoms include:
-
Sudden pain that begins on the lower right side of the abdomen
-
Pain that starts near the belly button and shifts to the lower right abdomen
-
Pain that worsens with coughing, walking or sudden movements
-
Nausea and vomiting
-
Loss of appetite
-
Low-grade fever that may worsen over time
-
Constipation or diarrhea
-
Abdominal bloating
-
Difficulty passing gas
The location of pain may differ depending on age and the position of the appendix. During pregnancy, pain may be felt in the upper abdomen because the appendix shifts upward.
Causes
Appendicitis most often occurs when the lining of the appendix, called the lumen, becomes blocked. This blockage can lead to infection.
When bacteria multiply rapidly inside the blocked appendix, it becomes inflamed, swollen and filled with pus. Without prompt treatment, the appendix may rupture, allowing infection to spread within the abdomen.
Risk factors
Appendicitis can affect anyone, but certain factors increase risk, including:
-
Age, with the highest risk between 10 and 30 years
-
Sex, as males have a slightly higher risk than females
Complications
If not treated promptly, appendicitis can lead to serious complications.
Possible complications include:
-
A ruptured appendix, which spreads infection throughout the abdomen and causes peritonitis, a life-threatening condition requiring emergency surgery
-
Formation of an abscess, which is a pocket of pus that develops in the abdomen after the appendix bursts
In cases of an abscess, treatment may involve draining the infection with a tube and using antibiotics. The appendix may be removed immediately or after the infection has cleared.
Prevention
There is no guaranteed way to prevent appendicitis. However, some evidence suggests that a diet high in fiber may reduce the risk.
General preventive measures include:
-
Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables and whole grains
-
Seeking prompt medical care for persistent or severe abdominal pain
Early diagnosis and treatment are important to prevent complications and ensure the best outcome.
Advertisement