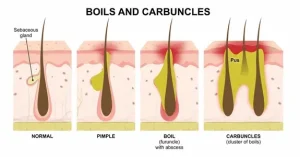
Overview
Boils and carbuncles are common bacterial skin infections that develop in hair follicles or oil glands. A boil, also known as a furuncle, is a painful, pus-filled lump that forms under the skin. A carbuncle is a cluster of interconnected boils that develop in a deeper layer of the skin and often drain pus from multiple openings.
These infections are usually caused by bacteria entering the skin through small cuts, insect bites, or irritated hair follicles. Boils and carbuncles can occur anywhere on the body but are most common on the face, neck, armpits, thighs, and buttocks.
Symptoms
Symptoms vary depending on the severity of the infection. Common symptoms include:
-
Red, swollen, and painful lumps under the skin
-
A lump that gradually fills with pus
-
Warmth and tenderness around the affected area
-
White or yellow center that may rupture and drain
-
Fever and general discomfort, especially with carbuncles
Carbuncles are more likely than single boils to cause fatigue or a feeling of being unwell.
Causes
Boils and carbuncles are most often caused by bacterial infection, commonly involving Staphylococcus aureus. The bacteria enter the skin through minor breaks and infect the hair follicle, leading to inflammation and pus formation.
Contributing causes include:
-
Poor skin hygiene
-
Frequent friction or pressure on the skin
-
Ingrown hairs
-
Existing skin conditions that damage the skin barrier
The infection may spread to nearby follicles, resulting in a carbuncle.
Risk Factors
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing boils and carbuncles. These include:
-
Close contact with someone who has a boil
-
Weakened immune system
-
Diabetes
-
Poor nutrition
-
Crowded or unsanitary living conditions
-
Repeated skin irritation or shaving
People with recurrent boils may carry bacteria on their skin or in the nose.
Complications
Most boils heal without problems, but complications can occur in severe or untreated cases. These may include:
-
Spread of infection to surrounding skin or deeper tissues
-
Formation of abscesses
-
Scarring after healing
-
Bloodstream infection in rare cases
-
Recurrence of boils over time
Prompt treatment reduces the risk of complications.
Prevention
Boils and carbuncles can often be prevented by maintaining good hygiene and skin care. Preventive measures include:
-
Washing hands and skin regularly with soap and water
-
Keeping cuts and wounds clean and covered
-
Avoiding sharing personal items such as towels or razors
-
Managing underlying health conditions like diabetes
-
Wearing loose-fitting clothing to reduce skin friction
Early care of minor skin injuries and attention to cleanliness can help prevent these infections.
Advertisement