Overview
Botulism is a rare but serious illness caused by toxins produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. These toxins attack the body’s nerves and can cause paralysis, breathing difficulties, and life-threatening complications. Botulism can occur through contaminated food, wounds, or exposure in infants, and it requires immediate medical attention.
Symptoms
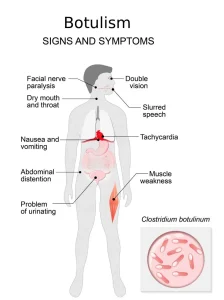
Symptoms of botulism usually begin within hours to days after exposure and often worsen rapidly.
• Difficulty swallowing or speaking
• Dry mouth
• Blurred or double vision
• Drooping eyelids
• Facial weakness on both sides of the face
• Muscle weakness that spreads from the head to the arms, legs, and torso
• Difficulty breathing
• Nausea, vomiting, or abdominal cramps in some cases
• Constipation in infants, often an early sign
Causes
Botulism is caused by exposure to botulinum toxin, which can enter the body in different ways depending on the type.
• Eating improperly preserved or contaminated foods
• Growth of Clostridium botulinum bacteria in wounds
• Ingestion of spores by infants, commonly from honey or soil
• Medical or cosmetic use of botulinum toxin in rare overdose situations
Risk factors
Certain situations increase the risk of developing botulism.
• Consuming home-canned or improperly stored foods
• Eating fermented, smoked, or preserved foods prepared without proper safety measures
• Having deep or contaminated wounds
• Injecting drugs using non-sterile needles
• Infants younger than one year exposed to honey or environmental spores
Complications
Botulism can cause severe and long-lasting complications if not treated promptly.
• Respiratory failure requiring mechanical ventilation
• Long-term muscle weakness and fatigue
• Difficulty speaking or swallowing for months
• Secondary infections due to prolonged hospitalization
• Death in severe untreated cases
Prevention
Botulism can often be prevented through proper food handling and safety practices.
• Follow safe home-canning and food preservation guidelines
• Avoid consuming bulging, leaking, or foul-smelling canned foods
• Refrigerate foods properly and reheat them thoroughly before eating
• Do not give honey to infants under one year of age
• Clean wounds promptly and seek medical care for deep or infected wounds
• Use medical and cosmetic botulinum toxin only under professional supervision
Advertisement