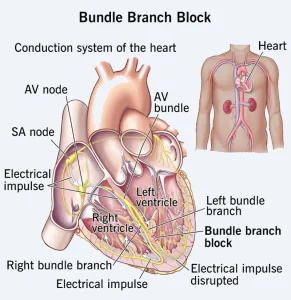
Overview
Bundle branch block is a heart condition in which there is a delay or blockage along the electrical pathways that help control the heartbeat. These pathways, called bundle branches, carry electrical impulses to the left and right sides of the heart’s lower chambers. When a bundle branch block occurs, the heart may beat out of sync, which can affect how efficiently it pumps blood. The condition may be discovered during routine testing and can be harmless or related to underlying heart disease.
Symptoms
Many people with bundle branch block have no noticeable symptoms. When symptoms do occur, they may include:
-
Dizziness or lightheadedness
-
Fainting or near-fainting episodes
-
Fatigue or weakness
-
Shortness of breath during activity
-
Slow or irregular heartbeat
Symptoms are more likely if the condition affects overall heart function or is associated with other heart problems.
Causes
Bundle branch block occurs when the electrical conduction system of the heart is damaged or disrupted. Possible causes include:
-
Heart attack or previous heart damage
-
High blood pressure affecting the heart muscle
-
Cardiomyopathy or heart muscle disease
-
Congenital heart conditions
-
Inflammation or infection of the heart tissue
-
Age-related changes in the heart’s electrical system
In some cases, no clear cause is identified.
Risk factors
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing bundle branch block:
-
Older age
-
History of heart disease or heart attack
-
High blood pressure
-
Structural abnormalities of the heart
-
Family history of heart rhythm disorders
The risk may vary depending on whether the left or right bundle branch is affected.
Complications
Bundle branch block itself may not cause complications, but problems can arise when it is linked to other heart conditions:
-
Worsening heart failure symptoms
-
Increased risk of abnormal heart rhythms
-
Reduced efficiency of the heart’s pumping action
-
Fainting-related injuries
-
Increased risk of cardiac events in severe cases
The outlook depends largely on the underlying cause and overall heart health.
Prevention
Not all cases of bundle branch block can be prevented, but certain measures may reduce risk or limit progression:
-
Managing high blood pressure and heart disease
-
Maintaining a heart-healthy lifestyle with balanced diet and exercise
-
Avoiding tobacco use
-
Following medical advice for existing heart conditions
-
Regular heart checkups, especially for those at higher risk
Early detection and proper management of heart conditions play an important role in reducing complications associated with bundle branch block.
Advertisement