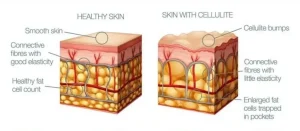
Overview
Cellulite is a common cosmetic condition in which the skin appears dimpled or lumpy, typically affecting the thighs, hips, buttocks, and abdomen. It occurs when fat deposits push through the connective tissue beneath the skin, creating an uneven surface. Cellulite is more common in women than men due to differences in fat distribution, connective tissue, and hormonal factors. While it is not a medical health risk, it can cause cosmetic concern for many individuals.
Symptoms
Cellulite is primarily identified by changes in the skin’s appearance rather than physical discomfort.
Common symptoms include:
-
Dimpled or lumpy skin, often described as “orange peel” or “cottage cheese” texture
-
Skin that appears uneven when pinched or flexed
-
Mild swelling or tenderness in some cases
Cellulite is usually painless, though in rare cases it may cause mild discomfort or sensitivity in affected areas.
Causes
Cellulite develops due to the interaction of fat cells, connective tissue, and skin structure. Several factors contribute to its formation.
Major causes include:
-
Accumulation of fat beneath the skin
-
Weakening or changes in connective tissue
-
Hormonal changes, particularly estrogen
-
Poor circulation and fluid retention
Genetic predisposition and lifestyle factors also influence the severity of cellulite.
Risk Factors
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing visible cellulite.
Key risk factors include:
-
Female sex
-
Age-related skin changes and reduced elasticity
-
Genetic predisposition
-
Sedentary lifestyle
-
Poor diet high in fat or sugar
-
Hormonal changes during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause
-
Rapid weight gain or obesity
Complications
Cellulite is primarily a cosmetic concern and is not associated with serious medical complications.
Potential issues may include:
-
Reduced self-confidence or body image concerns
-
Emotional distress or anxiety related to appearance
It does not indicate underlying disease or increase health risks.
Prevention
While cellulite cannot always be completely prevented, certain measures may help reduce its appearance or delay its development.
Preventive strategies include:
-
Maintaining a healthy weight and balanced diet
-
Regular physical activity, including strength training and cardiovascular exercise
-
Staying hydrated to support skin elasticity
-
Avoiding smoking, which can affect skin health
-
Managing hormonal changes with medical guidance if necessary
Consistent lifestyle measures may improve skin tone and minimize the visibility of cellulite over time.
Advertisement