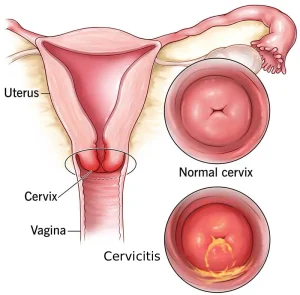
Overview
Cervicitis is inflammation of the cervix, the lower part of the uterus that opens into the vagina. It is a common gynecological condition and may be caused by infections, irritation, or allergic reactions. Cervicitis can occur in women of all ages and may be acute or chronic. In some cases, it causes noticeable symptoms, while in others it may be detected only during a routine pelvic examination.
Symptoms
Some individuals with cervicitis may have no symptoms, while others experience mild to moderate discomfort.
Common symptoms include:
-
Abnormal vaginal discharge
-
Vaginal itching or irritation
-
Pain during sexual intercourse
-
Pelvic discomfort or lower abdominal pain
Other possible symptoms include:
-
Bleeding between menstrual periods
-
Bleeding after sexual intercourse
-
Pain or burning sensation during urination
Causes
Cervicitis can develop due to infectious or non-infectious factors that irritate or infect the cervix.
Major causes include:
-
Sexually transmitted infections such as chlamydia, gonorrhea, or trichomoniasis
-
Bacterial imbalance in the vagina
-
Viral infections such as herpes simplex virus
-
Allergic reactions to latex condoms, spermicides, or feminine hygiene products
-
Physical irritation from tampons, diaphragms, or cervical caps
Risk Factors
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing cervicitis.
Key risk factors include:
-
Unprotected sexual activity
-
Multiple sexual partners
-
History of sexually transmitted infections
-
Early onset of sexual activity
-
Use of irritating vaginal products
-
Weakened immune system
Complications
If left untreated, cervicitis can lead to complications, particularly when caused by infection.
Possible complications include:
-
Spread of infection to the uterus or fallopian tubes
-
Pelvic inflammatory disease
-
Chronic pelvic pain
-
Increased risk of infertility
-
Higher susceptibility to acquiring or transmitting sexually transmitted infections
Early diagnosis and treatment reduce the risk of long-term complications.
Prevention
Preventing cervicitis focuses on reducing infection risk and avoiding cervical irritation.
Preventive strategies include:
-
Practicing safe sex and using barrier protection
-
Regular screening for sexually transmitted infections
-
Limiting the number of sexual partners
-
Avoiding douching and harsh vaginal products
-
Following medical advice for treatment of vaginal infections
Routine gynecological care and prompt treatment of infections play an important role in preventing cervicitis and its complications.
Advertisement