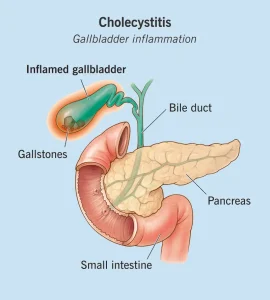
Overview
Cholecystitis is inflammation of the gallbladder, a small organ located beneath the liver that stores bile used for digestion. The condition most commonly occurs when gallstones block the cystic duct, causing bile to build up and irritate the gallbladder lining. Cholecystitis can be acute, developing suddenly, or chronic, resulting from repeated episodes of inflammation. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are important to prevent serious complications.
Symptoms
Symptoms of cholecystitis often appear suddenly and may be severe, especially in acute cases.
Common symptoms include:
-
Severe pain in the upper right or middle abdomen
-
Pain that may radiate to the right shoulder or back
-
Tenderness over the abdomen
-
Nausea and vomiting
-
Fever
Other possible symptoms include:
-
Bloating or indigestion
-
Loss of appetite
-
Abdominal pain that worsens after eating fatty foods
Causes
Cholecystitis is most often caused by obstruction of bile flow from the gallbladder, leading to inflammation.
Major causes include:
-
Gallstones blocking the cystic duct
-
Bile sludge buildup
-
Gallbladder infection
-
Reduced blood flow to the gallbladder
-
Tumors blocking bile ducts in rare cases
When bile cannot drain properly, it causes pressure, irritation, and inflammation of the gallbladder.
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the risk of developing cholecystitis, particularly those associated with gallstone formation.
Key risk factors include:
-
Gallstones
-
Obesity or rapid weight loss
-
Pregnancy
-
Increasing age
-
Female sex
-
High-fat or high-cholesterol diet
-
Diabetes
-
Prolonged fasting or critical illness
Complications
Untreated cholecystitis can lead to serious and potentially life-threatening complications.
Possible complications include:
-
Gallbladder rupture
-
Gangrene of the gallbladder
-
Abscess formation
-
Spread of infection to the bloodstream
-
Chronic gallbladder inflammation
-
Digestive problems after recurrent attacks
Severe cases may require emergency medical intervention.
Prevention
While not all cases of cholecystitis can be prevented, certain measures can reduce the risk.
Preventive strategies include:
-
Maintaining a healthy weight
-
Avoiding rapid weight loss or extreme dieting
-
Eating a balanced diet low in unhealthy fats
-
Staying physically active
-
Managing underlying conditions such as diabetes
-
Seeking medical care for early gallbladder symptoms
Early recognition and treatment of gallstones and gallbladder inflammation help reduce the risk of complications associated with cholecystitis.
Advertisement