Overview
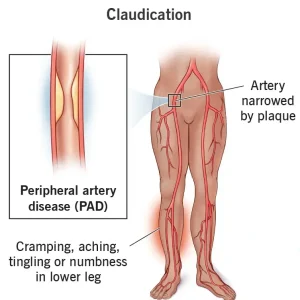
Claudication is a condition characterized by muscle pain, cramping, or fatigue that occurs during physical activity and improves with rest. It most commonly affects the legs and is usually a symptom of peripheral artery disease, a condition in which narrowed or blocked arteries reduce blood flow to the muscles.
The pain typically appears during walking or exercise and subsides within minutes of stopping. Claudication is an important warning sign of underlying vascular disease and is associated with an increased risk of heart attack and stroke.
Symptoms
Symptoms of claudication vary depending on the severity of blood flow restriction and the location of affected arteries.
Common symptoms include:
-
Cramping or aching pain in the calves, thighs, hips, or buttocks
-
Pain triggered by walking or physical activity
-
Relief of pain with rest
-
Muscle weakness or heaviness in the legs
-
Numbness or tingling in the lower limbs
-
Coldness in the feet or legs
-
Slower hair or nail growth on the legs
In severe cases, pain may occur with minimal activity.
Causes
Claudication is most often caused by reduced blood flow to the muscles due to narrowed arteries.
Common causes include:
-
Atherosclerosis, the buildup of plaque in the arteries
-
Peripheral artery disease
-
Blood clots in the arteries
-
Arterial inflammation
-
Structural abnormalities of blood vessels
The reduced oxygen supply during activity leads to muscle pain and cramping.
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the risk of developing claudication.
These include:
-
Smoking
-
Diabetes
-
High blood pressure
-
High cholesterol
-
Older age
-
Obesity
-
Sedentary lifestyle
-
Family history of cardiovascular disease
The presence of multiple risk factors increases disease severity.
Complications
If left untreated, claudication can progress and lead to serious complications.
Possible complications include:
-
Reduced mobility and physical endurance
-
Worsening peripheral artery disease
-
Non-healing sores or ulcers on the feet
-
Increased risk of limb ischemia
-
Higher risk of heart attack and stroke
Early diagnosis and management are essential to prevent progression.
Prevention
Claudication can often be prevented or its progression slowed by addressing underlying vascular risk factors.
Preventive strategies include:
-
Quitting smoking
-
Managing blood sugar levels in diabetes
-
Controlling blood pressure and cholesterol
-
Engaging in regular, supervised exercise
-
Maintaining a healthy weight
-
Eating a heart-healthy diet
-
Attending regular medical checkups
Lifestyle changes and early treatment play a crucial role in improving symptoms and reducing cardiovascular risk associated with claudication.
Advertisement