Overview
Constipation is a common digestive condition characterized by infrequent bowel movements, difficulty passing stools, or hard and dry stools. It can occur at any age and may be temporary or chronic. Constipation often results from dietary habits, lifestyle factors, or underlying medical conditions and can significantly affect comfort and quality of life.
Symptoms
Symptoms of constipation vary in severity and may include:
-
Fewer than three bowel movements per week
-
Hard, dry, or lumpy stools
-
Straining during bowel movements
-
Sensation of incomplete bowel emptying
-
Abdominal discomfort, bloating, or cramping
-
Rectal pain or pressure
-
Reduced appetite in some cases
Causes
Constipation occurs when stool moves too slowly through the digestive tract, allowing excessive water absorption. Common causes include low fiber intake, inadequate fluid consumption, lack of physical activity, and changes in routine. Certain medications, medical conditions, and hormonal changes can also contribute to constipation.
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing constipation:
-
Diet low in fiber
-
Inadequate fluid intake
-
Sedentary lifestyle
-
Older age
-
Pregnancy
-
Use of certain medications such as opioids or antidepressants
-
Underlying conditions like diabetes or thyroid disorders
Complications
If constipation is persistent or severe, it may lead to complications:
-
Hemorrhoids from straining
-
Anal fissures
-
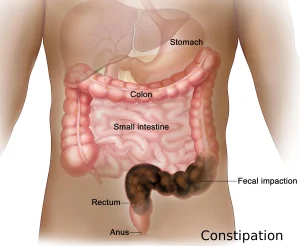
Fecal impaction
-
Rectal prolapse
-
Worsening abdominal discomfort
-
Reduced quality of life due to chronic symptoms
Prevention
Constipation can often be prevented or managed through lifestyle and dietary changes:
-
Eating a fiber-rich diet with fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
-
Drinking adequate amounts of water
-
Engaging in regular physical activity
-
Establishing a consistent bowel routine
-
Responding promptly to the urge to have a bowel movement
-
Managing underlying medical conditions that contribute to constipation
Advertisement