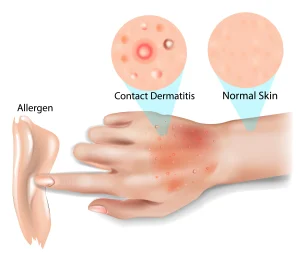
Overview
Contact dermatitis is an inflammatory skin condition that occurs when the skin comes into direct contact with a substance that causes irritation or triggers an allergic reaction. It is not contagious and can affect people of all ages. Contact dermatitis is commonly classified into irritant contact dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis, depending on the underlying cause.
Symptoms
Symptoms of contact dermatitis usually appear on the area of skin exposed to the offending substance and may vary in severity. Common symptoms include:
-
Redness and inflammation of the skin
-
Itching, burning, or stinging sensation
-
Swelling of the affected area
-
Dry, cracked, or scaly skin
-
Blisters or oozing in more severe cases
-
Skin thickening with repeated exposure
Causes
Contact dermatitis develops when the skin reacts to external substances. Irritant contact dermatitis results from direct damage to the skin by substances such as soaps, detergents, chemicals, or solvents. Allergic contact dermatitis occurs when the immune system reacts to allergens like nickel, fragrances, cosmetics, latex, or certain plants. Repeated or prolonged exposure increases the likelihood of developing symptoms.
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the risk of contact dermatitis:
-
Frequent exposure to irritants or allergens
-
Occupations involving chemicals, cleaning agents, or frequent hand washing
-
History of allergies, asthma, or eczema
-
Sensitive or damaged skin barrier
-
Use of certain cosmetics, jewelry, or personal care products
Complications
Although contact dermatitis is usually manageable, complications may occur:
-
Secondary skin infections from scratching
-
Chronic dermatitis with skin thickening and discoloration
-
Persistent itching affecting sleep and daily activities
-
Spread of rash if exposure continues
-
Scarring in severe or untreated cases
Prevention
Preventive measures focus on minimizing skin exposure to known irritants and allergens:
-
Identifying and avoiding triggering substances
-
Using protective gloves or clothing when handling chemicals
-
Choosing fragrance-free and hypoallergenic skin products
-
Moisturizing regularly to maintain the skin barrier
-
Washing skin promptly after contact with potential irritants
Advertisement