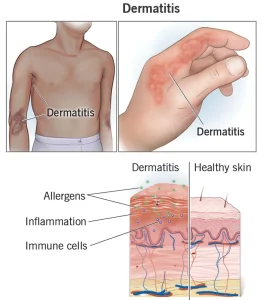
Overview
Diagnosis
To diagnose dermatitis, your doctor will carefully examine your skin and discuss your symptoms and medical history. This helps identify the type of dermatitis and rule out other possible skin conditions.
In some cases, a skin biopsy may be performed. This involves removing a small piece of skin for laboratory testing to confirm the diagnosis and exclude other diseases.
Patch testing
If your doctor suspects that your dermatitis is caused by an allergic reaction, a patch test may be recommended. In this test:
-
Small amounts of potential allergens are placed on adhesive patches.
-
These patches are applied to your skin, usually on the back, for 2 to 3 days.
-
During this period, you need to keep the area dry.
-
After removal, your doctor examines your skin for reactions under the patches to identify specific allergens that may be triggering your symptoms.
Treatment
The treatment for dermatitis depends on its cause, severity, and symptoms. If home remedies such as moisturizing and avoiding irritants do not provide relief, your doctor may recommend medical treatments such as:
-
Prescription-strength corticosteroid creams, gels, or ointments to reduce inflammation.
-
Creams or ointments containing calcineurin inhibitors, which help control immune system activity.
-
Controlled exposure to natural or artificial light, known as light therapy or phototherapy.
-
Prescription medications in the form of pills or injections, such as oral corticosteroids or a biologic treatment like dupilumab, for severe cases.
-
Wet dressings for severe atopic dermatitis, which involves applying corticosteroid ointment to the affected skin, wrapping it with moist bandages, and covering it with dry gauze to enhance healing and reduce itching.
Effective dermatitis management often requires a combination of medical treatment and consistent skin care, along with identifying and avoiding triggers that worsen symptoms.
Advertisement