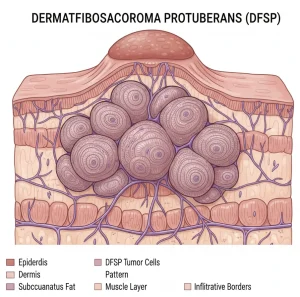
Overview
Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans is a rare, slow-growing soft tissue cancer that originates in the deep layers of the skin, particularly the dermis and subcutaneous tissue. It typically presents as a firm skin lesion that gradually enlarges over time. Although it grows slowly and rarely spreads to distant organs, it has a high tendency to recur locally if not treated adequately.
Symptoms
Symptoms often develop gradually and may be overlooked in early stages:
-
Firm, thickened skin patch or plaque
-
Reddish-brown, pink, or purplish skin discoloration
-
Painless lump that slowly increases in size
-
Raised or nodular growth in later stages
-
Skin that feels hard or rubbery to touch
-
Occasional tenderness as the tumor enlarges
Causes
The exact cause is not fully understood, but genetic changes play a key role:
-
Abnormal rearrangement of chromosomes involving collagen-producing cells
-
Overproduction of growth signals leading to uncontrolled cell growth
-
Sporadic genetic mutation rather than inherited condition
-
Rare association with previous skin injury or scarring
Risk Factors
Certain factors may increase the likelihood of developing this condition:
-
Young to middle-aged adults
-
Slight male predominance
-
History of skin trauma or surgical scars
-
Genetic mutations affecting connective tissue cells
-
Delayed diagnosis due to slow progression
Complications
If not treated properly, dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans may lead to:
-
Local tissue destruction
-
High risk of recurrence after incomplete removal
-
Functional impairment depending on tumor location
-
Cosmetic deformity
-
Rare transformation into a more aggressive form
-
Emotional distress related to chronic disease management
Prevention
There are no established methods to prevent dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, but early detection improves outcomes:
-
Monitoring persistent or enlarging skin lesions
-
Seeking medical evaluation for unexplained skin lumps
-
Early biopsy of suspicious or changing skin growths
-
Regular follow-up after treatment to detect recurrence
-
Prompt management of recurrent lesions
Advertisement