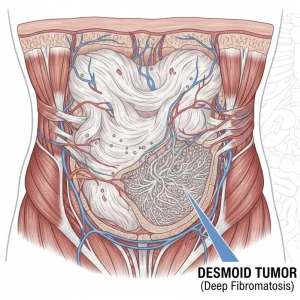
Overview
Desmoid tumors, also known as aggressive fibromatosis, are rare, noncancerous growths that arise from connective tissue, particularly fibrous tissue in muscles, tendons, or ligaments. Although they do not spread to distant organs, desmoid tumors can grow aggressively into surrounding tissues and cause significant local damage. They can occur anywhere in the body and may recur after treatment.
Symptoms
Symptoms depend on the tumor’s size and location and may develop gradually:
-
Firm or painless lump under the skin
-
Localized pain or discomfort
-
Swelling in the affected area
-
Restricted movement if the tumor involves muscles or joints
-
Abdominal pain or digestive symptoms when occurring in the abdomen
-
Nerve compression symptoms such as numbness or weakness
Causes
The exact cause of desmoid tumors is not fully understood, but several factors are associated with their development:
-
Genetic mutations affecting connective tissue cells
-
Abnormal regulation of cell growth
-
Prior surgery or physical trauma
-
Hormonal influences, particularly estrogen
-
Association with certain inherited conditions such as familial adenomatous polyposis
Risk Factors
Certain factors may increase the risk of developing desmoid tumors:
-
Young adults
-
Female sex
-
Pregnancy or recent childbirth
-
History of abdominal surgery
-
Genetic syndromes affecting the colon
-
Family history of desmoid tumors
Complications
Desmoid tumors can lead to serious complications despite being noncancerous:
-
Local tissue invasion and damage
-
Compression of nerves, blood vessels, or organs
-
Chronic pain
-
Impaired mobility or organ function
-
Recurrence after treatment
-
Psychological distress due to chronic disease management
Prevention
There are no proven methods to prevent desmoid tumors, but early detection and monitoring are important:
-
Regular follow-up for individuals with genetic risk factors
-
Monitoring new or enlarging soft tissue masses
-
Seeking medical evaluation for persistent or unexplained lumps
-
Careful surgical planning to reduce recurrence risk
-
Long-term surveillance after treatment
Advertisement