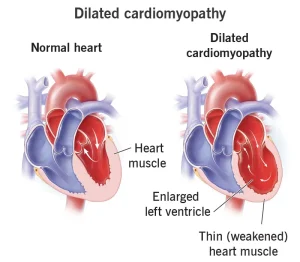
Overview
Dilated cardiomyopathy is a heart muscle disorder in which the heart’s main pumping chamber becomes enlarged and weakened. This reduces the heart’s ability to pump blood efficiently to the rest of the body. The condition can develop at any age and may progress gradually or appear suddenly. Dilated cardiomyopathy is a common cause of heart failure and abnormal heart rhythms.
Symptoms
Symptoms vary depending on disease severity and may worsen over time:
-
Shortness of breath during activity or at rest
-
Fatigue and weakness
-
Swelling of the legs, ankles, feet, or abdomen
-
Rapid or irregular heartbeat
-
Chest discomfort
-
Dizziness or lightheadedness
-
Difficulty exercising
-
Persistent cough, especially when lying down
Causes
Dilated cardiomyopathy can result from various factors that damage the heart muscle:
-
Genetic or inherited heart muscle disorders
-
Viral infections affecting the heart
-
Long-term high blood pressure
-
Coronary artery disease
-
Excessive alcohol consumption
-
Certain chemotherapy drugs or toxins
-
Metabolic disorders such as thyroid disease
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing dilated cardiomyopathy:
-
Family history of cardiomyopathy
-
Middle age, though it can occur at any age
-
Long-term alcohol or substance use
-
Chronic high blood pressure
-
Previous heart infections
-
Certain systemic diseases
Complications
If not properly managed, dilated cardiomyopathy may lead to serious complications:
-
Heart failure
-
Abnormal heart rhythms
-
Blood clots
-
Stroke
-
Sudden cardiac arrest
-
Progressive decline in heart function
Prevention
While not all cases can be prevented, some strategies may reduce risk or slow progression:
-
Managing blood pressure and heart disease risk factors
-
Limiting alcohol intake
-
Avoiding illicit drug use
-
Seeking early treatment for infections
-
Regular medical follow-up for those with a family history
-
Maintaining a heart-healthy lifestyle
Advertisement