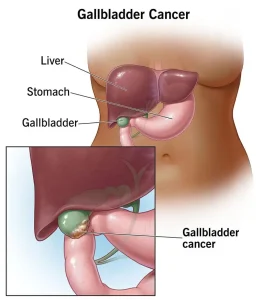
Overview
Gallbladder cancer is a rare but serious type of cancer that begins in the gallbladder, a small organ located beneath the liver that stores bile. This cancer often develops silently, with few or no symptoms in its early stages, which is why it is frequently diagnosed at an advanced stage. Gallbladder cancer is more common in older adults and tends to progress aggressively once it spreads to nearby organs such as the liver or bile ducts.
Symptoms
Symptoms of gallbladder cancer usually appear in later stages and may overlap with other gallbladder conditions. Common symptoms include:
-
Persistent pain in the upper right abdomen
-
Unexplained weight loss
-
Loss of appetite
-
Nausea or vomiting
-
Jaundice, including yellowing of the skin and eyes
-
Abdominal bloating or swelling
-
Fever without a clear cause
Causes
The exact cause of gallbladder cancer is not always known, but it is believed to develop from long-term irritation and inflammation of the gallbladder lining. Contributing factors may include:
-
Chronic gallbladder inflammation
-
Gallstones causing repeated irritation
-
Abnormal growths such as gallbladder polyps
-
Genetic changes affecting cell growth and division
These factors may lead to abnormal cell changes that eventually become cancerous.
Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the risk of developing gallbladder cancer, including:
-
Presence of gallstones, especially large or long-standing stones
-
Chronic gallbladder infection or inflammation
-
Gallbladder polyps larger than one centimeter
-
Older age
-
Female sex
-
Family history of gallbladder or biliary tract cancers
-
Obesity
Complications
Gallbladder cancer can lead to serious complications, particularly if not diagnosed early. Possible complications include:
-
Spread of cancer to the liver, bile ducts, or nearby organs
-
Bile duct obstruction causing severe jaundice
-
Digestive problems due to impaired bile flow
-
Severe abdominal pain and reduced quality of life
Advanced disease may significantly limit treatment options and affect survival.
Prevention
There is no guaranteed way to prevent gallbladder cancer, but certain steps may help reduce risk:
-
Managing gallstones through medical evaluation and treatment
-
Maintaining a healthy body weight
-
Following a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables
-
Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol use
-
Seeking medical advice for persistent abdominal pain or jaundice
Early detection and management of gallbladder-related conditions may help lower the risk of developing gallbladder cancer.
Advertisement