Overview
IgA nephropathy, also known as Berger disease, is a kidney disorder caused by the buildup of immunoglobulin A (IgA) antibodies in the glomeruli, the filtering units of the kidneys. This accumulation leads to inflammation and can impair the kidneys’ ability to filter waste from the blood. IgA nephropathy is one of the most common causes of glomerulonephritis worldwide and can affect individuals of any age, though it is more common in males and typically appears in the teens or twenties.
Symptoms
-
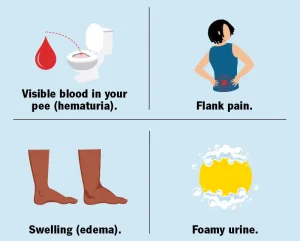
Blood in the urine (hematuria), which may appear pink, brown, or cola-colored
-
Protein in the urine (proteinuria)
-
Swelling in the hands, feet, or face (edema)
-
High blood pressure
-
Fatigue or feeling generally unwell
-
Occasionally, episodes of dark urine following respiratory or gastrointestinal infections
Causes
IgA nephropathy occurs when IgA antibodies, which normally help the body fight infections, accumulate in the kidneys and trigger inflammation. The exact cause is unknown, but factors may include:
-
Abnormal immune system response
-
Genetic predisposition
-
Infections, particularly respiratory or gastrointestinal, that trigger IgA production
-
Environmental factors influencing immune system activity
Risk factors
-
Age: Most commonly diagnosed in people aged 15–30
-
Gender: Males are more frequently affected
-
Family history of IgA nephropathy or other kidney disorders
-
Ethnicity: More common in Asian populations than in Caucasian or African populations
Complications
-
Chronic kidney disease leading to gradual loss of kidney function
-
High blood pressure
-
Nephrotic syndrome (excessive protein loss in urine)
-
End-stage kidney disease requiring dialysis or kidney transplantation in severe cases
-
Recurrent urinary tract infections or episodes of hematuria
Prevention
There is no guaranteed way to prevent IgA nephropathy, but measures to protect kidney health and manage risk factors include:
-
Regular monitoring of kidney function and blood pressure
-
Controlling high blood pressure through diet, exercise, and medications
-
Avoiding excessive use of medications that can harm the kidneys, such as NSAIDs
-
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet, adequate hydration, and avoiding smoking
-
Prompt treatment of infections to reduce immune triggers
Early diagnosis and ongoing management can help slow the progression of IgA nephropathy and reduce the risk of serious kidney complications.
Advertisement