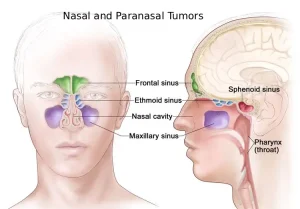
Overview
Nasal and paranasal tumors are abnormal growths that develop in the nasal cavity or the paranasal sinuses, which are air-filled spaces around the nose. These tumors can be benign or malignant and are relatively rare. Because the nasal cavity and sinuses are close to the eyes, brain, and important nerves, even noncancerous tumors can cause significant symptoms if they grow or spread. Early detection is often challenging, as symptoms may resemble common nasal or sinus conditions.
Symptoms
Symptoms depend on the size, location, and type of tumor and may develop gradually:
-
Persistent nasal blockage or congestion, often on one side
-
Nosebleeds that occur frequently or without clear cause
-
Facial pain, pressure, or swelling
-
Reduced or lost sense of smell
-
Nasal discharge that may be bloody or foul-smelling
-
Loosening of teeth or pain in the upper jaw
-
Eye symptoms such as swelling, double vision, or vision changes in advanced cases
Symptoms that do not improve with routine treatment should be medically evaluated.
Causes
The exact cause of nasal and paranasal tumors is not always known. These tumors arise from abnormal growth of cells lining the nasal cavity or sinuses. Long-term exposure to certain environmental or occupational substances can damage cells and increase the risk of abnormal changes. Both genetic and environmental factors are believed to play a role.
Risk Factors
Several factors are associated with a higher risk of developing nasal and paranasal tumors:
-
Long-term exposure to wood dust, leather dust, or textile fibers
-
Occupational exposure to chemicals such as formaldehyde or nickel
-
Tobacco use
-
Chronic sinus inflammation or infections
-
Certain viral infections
-
Male sex and older age
Occupational safety measures are important for those at increased risk.
Complications
If left untreated, nasal and paranasal tumors can lead to serious complications:
-
Local tissue destruction affecting the nose, sinuses, or facial bones
-
Spread of tumor to the eyes, brain, or nearby nerves
-
Vision loss or neurological symptoms
-
Breathing difficulties due to airway obstruction
-
Recurrence after treatment, depending on tumor type
Early diagnosis helps reduce the likelihood of severe complications.
Prevention
Not all nasal and paranasal tumors can be prevented, but certain measures may lower risk:
-
Avoiding tobacco use
-
Using protective equipment in high-risk occupations
-
Reducing exposure to harmful dusts and chemicals
-
Managing chronic sinus conditions under medical guidance
-
Seeking evaluation for persistent nasal symptoms
Awareness of risk factors and early medical attention play a key role in prevention and improved outcomes for nasal and paranasal tumors.
Advertisement