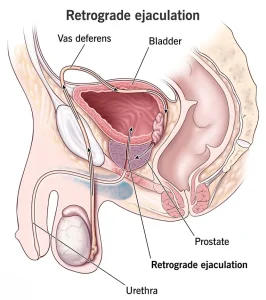
Overview
Retrograde ejaculation is a condition in which semen flows backward into the bladder instead of exiting through the penis during ejaculation. As a result, little or no semen is released despite the sensation of orgasm. This condition is not usually harmful to overall health but can affect male fertility and cause emotional distress. It is most commonly seen in adult men and is often related to nerve or muscle dysfunction.
Symptoms of Retrograde Ejaculation
The signs of retrograde ejaculation are usually noticeable during sexual activity or afterward.
-
Little or no semen released during orgasm
-
Cloudy urine after ejaculation due to the presence of semen in the bladder
-
Normal sexual desire and ability to achieve orgasm
-
Difficulty achieving pregnancy due to reduced or absent semen output
Causes of Retrograde Ejaculation
Retrograde ejaculation occurs when the bladder neck muscles fail to close properly during ejaculation, allowing semen to enter the bladder.
Common causes include:
-
Nerve damage due to diabetes or neurological disorders
-
Side effects of certain medications, especially those used for high blood pressure or prostate conditions
-
Surgery involving the prostate, bladder, or urethra
-
Spinal cord injury or nerve-related conditions
Risk Factors for Retrograde Ejaculation
Certain conditions and treatments increase the likelihood of developing retrograde ejaculation.
-
Long-standing diabetes
-
Use of alpha-blocker medications
-
History of prostate or bladder surgery
-
Neurological diseases affecting nerve function
-
Aging, which may increase vulnerability to nerve damage
Complications of Retrograde Ejaculation
While not life-threatening, retrograde ejaculation can lead to reproductive and psychological challenges.
-
Male infertility or reduced fertility
-
Emotional stress, anxiety, or relationship concerns
-
Reduced satisfaction related to changes in ejaculation
The condition does not typically affect sexual pleasure or the ability to have erections.
Prevention of Retrograde Ejaculation
Preventive measures focus on managing underlying conditions and minimizing known risk factors.
-
Proper management of diabetes and blood sugar levels
-
Reviewing medications with a healthcare provider to adjust those affecting ejaculation
-
Careful surgical planning and nerve-sparing techniques when possible
-
Seeking early medical advice if changes in ejaculation are noticed
Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help manage symptoms and support fertility goals in men with retrograde ejaculation.
Advertisement