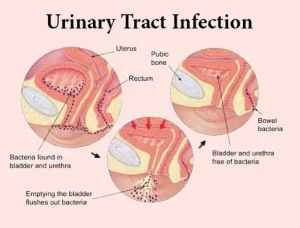
Overview
A urinary tract infection is an infection that affects any part of the urinary system, including the kidneys, ureters, bladder, or urethra. Most infections involve the lower urinary tract, particularly the bladder and urethra. Urinary tract infections are commonly caused by bacteria entering the urinary tract and multiplying. They are more frequent in women, but men, children, and older adults can also be affected. Prompt treatment is important to prevent the infection from spreading to the kidneys.
Symptoms
Symptoms of a urinary tract infection vary depending on the area involved and the individual.
Common symptoms may include:
-
A strong, persistent urge to urinate
-
Burning sensation during urination
-
Passing small amounts of urine frequently
-
Cloudy, dark, or strong-smelling urine
-
Blood in the urine
-
Pelvic pain in women
-
Lower abdominal discomfort
If the infection spreads to the kidneys, symptoms may also include fever, chills, nausea, vomiting, and back or side pain.
Causes
Urinary tract infections are most often caused by bacteria from the digestive tract entering the urinary system.
Possible causes include:
-
Bacteria entering the urethra and traveling to the bladder
-
Incomplete emptying of the bladder
-
Use of urinary catheters
-
Sexual activity
-
Blockages such as kidney stones
-
Changes in the urinary tract due to aging or medical conditions
Escherichia coli is the most common bacterial cause.
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the risk of developing a urinary tract infection.
Risk factors include:
-
Female anatomy, with a shorter urethra
-
Sexual activity
-
Pregnancy
-
Menopause
-
Use of urinary catheters
-
Diabetes
-
Urinary tract abnormalities
-
Enlarged prostate in men
Complications
Untreated urinary tract infections can lead to serious health problems.
Possible complications include:
-
Recurrent infections
-
Kidney infection and kidney damage
-
Sepsis in severe cases
-
Narrowing of the urethra in men
-
Pregnancy-related complications if untreated
Early treatment helps prevent long-term complications.
Prevention
Many urinary tract infections can be prevented with simple lifestyle measures.
Preventive steps may include:
-
Drinking plenty of fluids to flush bacteria from the urinary tract
-
Urinating regularly and not holding urine for long periods
-
Wiping from front to back after using the toilet
-
Urinating soon after sexual activity
-
Avoiding irritating feminine products
-
Maintaining good personal hygiene
Early recognition of symptoms and prompt treatment reduce the risk of complications and recurrence.
Advertisement