Overview
Aplastic anemia is a condition in which the bone marrow stops making enough new blood cells. This leads to a shortage of red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. As a result, people with aplastic anemia may feel very tired and are more likely to develop infections and uncontrolled bleeding.
Aplastic anemia is rare and can occur at any age. It may develop suddenly or appear gradually and worsen over time. The condition can range from mild to severe and may become life-threatening if not treated.
Treatment depends on the severity of the disease and may include medicines that suppress the immune system, blood transfusions, or a stem cell transplant, also known as a bone marrow transplant.
Symptoms
Some people with aplastic anemia may have no symptoms, especially in mild cases. When symptoms occur, they are related to low levels of blood cells.
Common symptoms include:
-
Fatigue
-
Shortness of breath
-
Rapid or irregular heartbeat
-
Frequent or prolonged infections
-
Easy or unexplained bruising
-
Nosebleeds or bleeding gums
-
Prolonged bleeding from cuts
-
Pale skin
-
Skin rash
-
Fever
Aplastic anemia may be short-lived or long-lasting. In severe cases, it can be serious and potentially fatal without proper treatment.
Causes
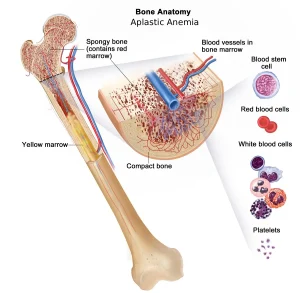
Bone marrow is a soft, spongy tissue inside the bones that produces stem cells. These stem cells develop into red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. In aplastic anemia, the stem cells are damaged, leading to reduced production of all types of blood cells.
The most common cause is the immune system mistakenly attacking the bone marrow stem cells. Other factors that can damage bone marrow include:
-
Radiation therapy and chemotherapy used for cancer treatment
-
Exposure to toxic chemicals such as pesticides, insecticides and benzene
-
Certain medicines, including some antibiotics and drugs used to treat rheumatoid arthritis
-
Autoimmune disorders in which the immune system attacks healthy tissues
-
Viral infections that affect the bone marrow, such as hepatitis, Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, parvovirus B19 and HIV
-
Pregnancy, in rare cases
-
Unknown causes, referred to as idiopathic aplastic anemia
Some people with aplastic anemia may also have other rare conditions. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria can occur alongside aplastic anemia or develop later. Fanconi anemia is a rare inherited disorder that leads to aplastic anemia and is usually diagnosed in childhood.
Risk factors
Aplastic anemia is uncommon, but certain factors can increase the risk, including:
-
Treatment with high-dose radiation or chemotherapy
-
Exposure to toxic chemicals
-
Use of specific prescription medicines
-
Certain blood disorders or autoimmune diseases
-
Serious viral infections
-
Pregnancy, in rare situations
Complications
If not properly managed, aplastic anemia can lead to serious complications, such as:
-
Severe or life-threatening infections
-
Excessive bleeding due to low platelet counts
-
Heart problems caused by severe anemia
-
Progression to other bone marrow disorders
-
Death in severe, untreated cases
Prevention
There is no known way to prevent most cases of aplastic anemia. However, reducing exposure to potential triggers may help lower risk. Preventive steps may include:
-
Avoiding contact with toxic chemicals such as insecticides, herbicides, organic solvents and paint removers
-
Using protective equipment when working with chemicals
-
Discussing potential side effects of medications with a healthcare professional
Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are important to improve outcomes and reduce the risk of complications.
Advertisement