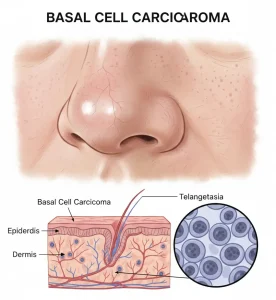
Overview
Diagnosis
To diagnose basal cell carcinoma, your healthcare professional will first ask about your medical history and examine your skin carefully.
Medical History
You may be asked several questions to understand your symptoms and risk factors, such as:
-
When did you first notice this growth or spot on your skin?
-
Has it changed in size, color, or shape?
-
Is it painful or itchy?
-
Have you had skin cancer before?
-
Does anyone in your family have a history of skin cancer?
-
How often do you use sunscreen or protect your skin from the sun?
-
Do you check your skin regularly for unusual changes?
Physical Examination
A thorough skin examination will be performed to identify any suspicious lesions or other areas of concern across your body.
Skin Biopsy
If a lesion looks suspicious, your healthcare provider may perform a skin biopsy. A small sample of the affected skin is removed and sent to a laboratory for testing. The results confirm whether the lesion is cancerous and identify its type.
The method of biopsy depends on the size and depth of the lesion.
Treatment
The goal of treating basal cell carcinoma is to remove the cancer completely and prevent recurrence. The right treatment depends on the tumor’s size, location, and whether it’s a first occurrence or recurrence.
Surgical Treatments
-
Surgical excision: The doctor removes the cancerous lesion along with a small margin of healthy skin. The tissue is checked under a microscope to ensure all cancer cells are gone. This method is often used for lesions on the chest, back, hands, or feet.
-
Mohs surgery: The cancer is removed layer by layer, and each layer is examined under a microscope. This precise technique preserves healthy skin and is ideal for cancers on the face or areas with higher recurrence risk.
Other Treatments
If surgery isn’t suitable, other treatment options may include:
-
Curettage and electrodessication (C&E): The surface of the cancer is scraped off, and heat is applied to destroy any remaining cells. Suitable for small lesions that are unlikely to recur.
-
Radiation therapy: High-energy beams are used to destroy cancer cells, often used when surgery is not possible.
-
Cryosurgery (freezing treatment): Liquid nitrogen is used to freeze and destroy cancer cells, usually for small or superficial lesions.
-
Topical medications: Prescription creams or gels can be used for early-stage or shallow basal cell carcinomas.
-
Photodynamic therapy: Combines a light-sensitive medication with light exposure to destroy cancer cells, often used for surface-level skin cancers.
Treatment for Advanced or Spreading Cancer
Although rare, basal cell carcinoma can spread to nearby lymph nodes or other parts of the body. In such cases, advanced treatments may include:
-
Targeted therapy: Uses medications that block specific molecules in cancer cells to stop their growth.
-
Immunotherapy: Boosts the immune system’s ability to recognize and attack cancer cells, used for advanced or metastatic cases.
Summary
Basal cell carcinoma is highly treatable, especially when detected early. Regular skin checks, sun protection, and follow-up with a dermatologist are essential for prevention and early detection. If you notice any unusual skin changes, consult a healthcare professional promptly for evaluation and treatment.
Advertisement