Overview
Bedbug Bites – Diagnosis and Treatment
Bedbug bites are itchy, red welts caused by small parasitic insects that feed on human blood. While their bites are uncomfortable, bedbugs are not known to spread disease. Identifying and eliminating the infestation is key to preventing further bites.
Diagnosis
If you suspect bedbugs are biting you, inspect your home immediately. Bedbugs usually hide in small crevices and come out at night, so nighttime inspection is often more effective.
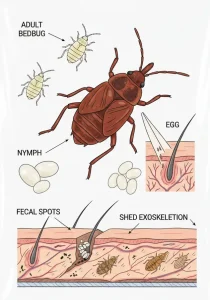
Check for the following signs:
-
Dark specks along mattress seams or furniture joints — these are bedbug droppings.
-
Pale yellow skin castings, which are empty shells left behind as bedbugs grow.
-
Rusty or reddish stains on bed sheets or mattresses caused by crushed bedbugs.
Inspect walls, furniture joints, mattress seams, bed frames, and headboards carefully. Bedbugs can also hide behind wallpaper, picture frames, and electrical outlets.
Treatment
Most bedbug bites heal naturally within one to two weeks without medical treatment. To relieve itching and discomfort, you may use:
-
A mild skin cream containing hydrocortisone, such as Cortaid.
-
An oral antihistamine, such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl), to reduce itching and allergic reactions.
If you develop an infection from scratching, consult a healthcare professional for appropriate care.
Treating Your Home
Eliminating bedbugs from your home can be challenging, as they are small, nocturnal, and can survive for months without feeding. A professional exterminator is often recommended. They typically use a combination of chemical and nonchemical methods to eradicate the infestation.
If you wish to manage the problem yourself, consider these steps:
-
Vacuuming: Carefully vacuum crevices, seams, and furniture surfaces. Dispose of the vacuum bag or contents immediately after use.
-
Laundering: Wash bedding, clothing, and fabrics in water at least 120°F (48.9°C) and dry them on high heat for at least 20 minutes.
-
Heat exposure: In hot climates, place infested items inside sealed plastic bags and leave them in a vehicle parked in direct sunlight for a day. The internal temperature should reach at least 120°F (48.9°C).
In severe infestations, you may need to discard heavily infested furniture such as mattresses or couches. Clearly mark discarded items as unusable to prevent others from taking them.
Advertisement