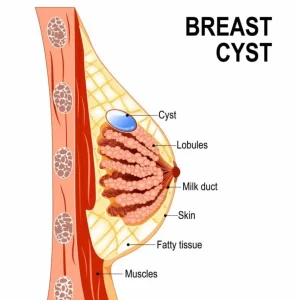
Overview
Diagnosis of Breast Cysts
Breast cyst diagnosis usually involves a combination of breast exam, imaging tests, and possibly fine-needle aspiration or biopsy.
-
Breast exam:
-
The doctor examines the breast for lumps or abnormalities.
-
A clinical breast exam alone cannot confirm a cyst, so further testing is needed.
-
-
Imaging tests:
-
Mammography: Detects large cysts or clusters of small cysts, but may miss microcysts.
-
Breast ultrasound: Distinguishes between fluid-filled cysts and solid lumps. Solid lumps may require further testing, including biopsy.
-
-
Fine-needle aspiration (FNA):
-
A thin needle is inserted into the lump to withdraw fluid, often guided by ultrasound.
-
Diagnosis is confirmed if the lump disappears after fluid removal.
-
Straw-colored, non-bloody fluid: No further treatment required.
-
Bloody fluid or persistent lump: Sent for lab testing and further evaluation by a breast specialist.
-
If no fluid is withdrawn, imaging or biopsy may be recommended to rule out solid masses.
-
Treatment of Breast Cysts
-
No treatment needed:
-
Simple, fluid-filled cysts that are asymptomatic usually require no intervention.
-
Many cysts disappear on their own.
-
-
Fine-needle aspiration:
-
Can both diagnose and treat cysts if all fluid is removed.
-
Some cysts may need repeated drainage if they recur.
-
Persistent cysts over 2–3 menstrual cycles or growing cysts should be reevaluated.
-
-
Hormone use:
-
Oral contraceptives may reduce recurrence of breast cysts in some women.
-
Hormone therapy like tamoxifen is usually reserved for severe symptoms.
-
Discontinuing hormone therapy after menopause may help prevent cysts.
-
-
Surgery:
-
Rarely required.
-
Considered if a cyst is painful, recurrent, or contains blood.
-
Advertisement