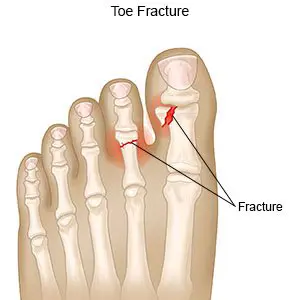
Overview
Diagnosis of a Broken Toe
-
During the physical exam, your healthcare provider will:
-
Check for tenderness in the toe.
-
Inspect the skin around the injury to ensure it’s not cut and that blood flow and nerve signals are intact.
-
-
X-rays of the foot are usually needed to confirm a broken toe.
Treatment of a Broken Toe
Medications
-
Pain can usually be managed with over-the-counter medicines such as:
-
Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB)
-
Naproxen sodium (Aleve)
-
Acetaminophen (Tylenol)
-
-
Severe pain may require prescription painkillers.
Reduction
-
If the broken bone pieces don’t fit together, your provider may perform a reduction:
-
Done without cutting the skin.
-
Ice or a local anesthetic may be used to numb the toe.
-
Keeping the Toe from Moving
-
Immobilization is key for healing. Options include:
-
Buddy taping: Taping the injured toe to a neighboring toe, using gauze or felt between them to prevent skin irritation.
-
Stiff-bottomed shoe: Provides support and prevents movement while allowing room for swelling.
-
Casting: A walking cast may be used if the bone pieces won’t stay in place.
-
Surgery
-
In some cases, a surgeon may use pins, plates, or screws to hold the bones in place during healing.
Advertisement