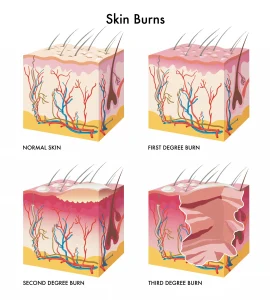
Overview
Burn Injury Diagnosis and Treatment Guide
Burn injuries range from minor to severe, and proper evaluation is essential for effective treatment and recovery.
Diagnosis of Burns
Healthcare professionals assess burns by examining the skin and affected areas. They determine the severity based on the depth, size, and location of the burn. Severe burns may require transfer to a specialized burn center, especially if the burn:
-
Covers more than 10% of total body surface area
-
Is very deep (full-thickness)
-
Occurs on the face, feet, groin, or major joints
-
Meets other criteria set by the American Burn Association
Your healthcare provider may also check for additional injuries and order tests such as X-rays, lab work, or other diagnostics to ensure comprehensive care.
First Aid for Burns
Minor burns can often be treated at home, while major burns require immediate medical attention. For severe burns, follow these first-aid steps until professional help arrives:
-
Remove the person from the source of the burn to prevent further injury
-
Ensure the person is breathing; begin rescue breathing if necessary
-
Remove rings, belts, or tight items around the burned area
-
Loosely cover the burn with a clean cloth or gauze
-
Elevate the burned area above heart level if possible
-
Monitor for shock symptoms: cool, clammy skin, weak pulse, or shallow breathing
Medical Treatment for Burns
Treatment for burns depends on severity, location, and patient health. Options may include:
Medications and Topical Treatments
-
Water-based treatments such as whirlpool baths to remove dead tissue
-
Intravenous fluids (IV fluids) to prevent dehydration and organ failure
-
Pain and anxiety medications like morphine for severe pain or during dressing changes
-
Burn creams and ointments such as silver sulfadiazine or bacitracin to prevent infection
-
Specialized dressings to protect wounds and promote healing
-
Antibiotics if infection occurs
-
Tetanus vaccination if recommended
Physical and Occupational Therapy
Burns affecting joints or large areas may require physical therapy to maintain flexibility and strength. Occupational therapy can help restore daily activities.
Surgical Interventions
Severe burns may require:
-
Breathing assistance for burns on the face or neck
-
Feeding tube for patients with large burns or poor nutrition
-
Escharotomy to relieve pressure from tight burn tissue
-
Skin grafts to replace damaged tissue with healthy skin from the patient, donors, or animals
Self-Care for Minor Burns
For minor burns, follow these guidelines:
-
Move away from the burn source and cool the area under running water for 10–20 minutes
-
Remove tight items like rings or watches
-
Apply soothing lotion such as aloe vera or cocoa butter after cooling
-
Cover with a clean, loosely wrapped bandage
-
Take over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen if needed
Avoid:
-
Using cold water or ice directly on the burn
-
Breaking blisters
-
Fluffy cotton bandages
-
Applying grease, butter, or topical painkillers
-
Removing clothing stuck to the burn
Recovery Tips
-
Use sunscreen and moisturizer on healed areas to protect skin
-
Follow up with a healthcare provider for serious burns
-
Consider ongoing physical or occupational therapy for large or joint-involved burns
This guide provides comprehensive information for burn diagnosis, first aid, medical care, and recovery to ensure safe healing and minimize complications.
Advertisement