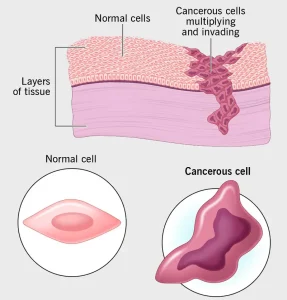
Overview
Diagnosis
Cancer diagnosis involves a detailed evaluation of symptoms, imaging tests, and laboratory investigations to detect abnormal cell growth. Early diagnosis is essential for better treatment outcomes and survival rates.
Common diagnostic steps include:
-
Physical examination to check for lumps, swelling, or unusual changes in the body.
-
Laboratory tests such as blood, urine, or tissue analysis to identify abnormal levels or substances.
-
Imaging tests like X-ray, CT scan, MRI, PET scan, or ultrasound to locate tumors or abnormal growths.
-
Biopsy, which involves removing a sample of tissue to examine under a microscope and confirm the presence of cancer cells.
-
Genetic testing to identify specific mutations that may cause certain cancers or influence treatment plans.
Treatment
Cancer treatment depends on the type, stage, and location of the cancer, as well as the patient’s overall health. The goal is to remove or destroy cancer cells and prevent them from spreading.
Main treatment options include:
-
Surgery to remove the tumor or affected tissue.
-
Radiation therapy using high-energy rays to target and kill cancer cells.
-
Chemotherapy that uses strong medications to destroy rapidly growing cancer cells.
-
Immunotherapy, which boosts the body’s immune system to fight cancer more effectively.
-
Targeted therapy focusing on specific genetic changes in cancer cells.
-
Hormone therapy to block or lower hormones that fuel certain types of cancers, such as breast or prostate cancer.
-
Stem cell transplant to restore bone marrow damaged by high-dose chemotherapy or radiation.
Prevention
Preventing cancer involves lifestyle changes and regular screenings to detect it early. Although not all cancers can be prevented, risk can be reduced significantly.
Effective prevention measures include:
-
Avoiding tobacco and limiting alcohol consumption.
-
Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
-
Maintaining a healthy weight and exercising regularly.
-
Protecting skin from excessive sun exposure by using sunscreen.
-
Getting vaccinated against cancer-related infections such as HPV and hepatitis B.
-
Undergoing routine screenings like mammograms, colonoscopies, and Pap tests for early detection.
Key Takeaway
Cancer is a group of diseases characterized by uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells that can spread throughout the body. Early diagnosis, timely treatment, and healthy lifestyle choices play a vital role in improving survival and quality of life.
Advertisement