Overview
Diagnosis
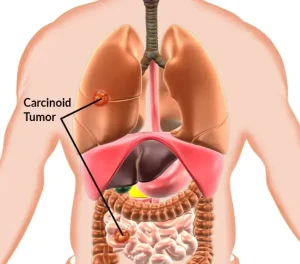
Carcinoid tumors are rare, slow-growing tumors that usually develop in the gastrointestinal tract, pancreas, or lungs. Diagnosis often begins with an evaluation of symptoms such as abdominal pain, flushing, diarrhea, or wheezing.
Common diagnostic tests include:
-
Blood tests: Detect tumor markers such as chromogranin A and serotonin levels
-
Urine tests: 24-hour collection to measure 5-HIAA, a breakdown product of serotonin
-
Imaging studies: CT scan, MRI, or PET scan to locate primary tumors and detect metastasis
-
Endoscopy: Visual examination of the gastrointestinal tract to find tumors
-
Biopsy: Tissue sample taken for microscopic examination to confirm the tumor type
Early diagnosis is important for reducing complications and planning effective treatment.
Treatment
Treatment of carcinoid tumors depends on the size, location, and spread of the tumor, as well as hormone-related symptoms.
Treatment options may include:
-
Surgery: Removal of primary tumors or metastases when feasible
-
Medications:
-
Somatostatin analogs (e.g., octreotide, lanreotide) to control hormone production
-
Targeted therapies to inhibit tumor growth or specific tumor pathways
-
-
Liver-directed therapies: Embolization or ablation for liver metastases
-
Radiation therapy: Occasionally used for tumors that cannot be removed surgically
-
Supportive care: Management of symptoms like diarrhea, flushing, and heart complications
A personalized treatment plan is critical for effective tumor control and symptom management.
Monitoring and Prevention
Although carcinoid tumors cannot always be prevented, regular monitoring helps detect growth or recurrence early.
Monitoring strategies include:
-
Routine blood and urine tests to track hormone levels
-
Imaging studies to check for tumor growth or metastasis
-
Managing diet and lifestyle factors that may worsen symptoms
-
Educating patients to recognize signs of complications early
Long-term follow-up with a healthcare provider ensures proper management and better outcomes.
Key Takeaway
Carcinoid tumors are rare hormone-secreting tumors that require careful evaluation for diagnosis. Treatment often involves surgery, medications, and targeted therapies to control symptoms and tumor growth. Early detection and continuous monitoring improve quality of life and prevent complications.
Advertisement