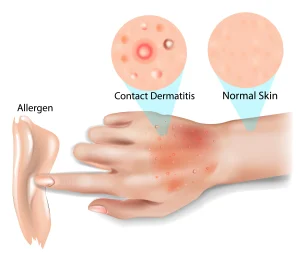
Overview
Diagnosis
Your health care provider may diagnose contact dermatitis by discussing your signs and symptoms, asking questions about your possible exposure to irritants or allergens, and performing a skin exam to assess the rash.
A patch test may be recommended to identify the cause of your rash. During this test, small amounts of possible allergens are placed on sticky patches, which are then applied to your skin—typically on your back. The patches remain in place for two to three days, and you’ll need to keep the area dry. Afterward, your health care provider checks the skin for reactions to determine whether any substances triggered your symptoms.
This test is especially useful if the cause of your rash is unclear or if your rash recurs frequently. However, redness and irritation can be more difficult to detect on brown or Black skin, which may occasionally lead to missed diagnoses.
Treatment
If self-care measures do not relieve symptoms, your health care provider may recommend medication such as:
-
Steroid creams or ointments to reduce itching and inflammation. Prescription options include clobetasol 0.05% or triamcinolone 0.1%. Follow your provider’s guidance on how often and how long to apply them.
-
Oral medications in more severe cases to reduce swelling, relieve itching, or treat any bacterial infection.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
To ease itching and soothe inflamed skin, consider these self-care steps:
-
Avoid the irritant or allergen by identifying and staying away from the triggering substance. Your provider can help you identify safe and unsafe products.
-
Apply 1% hydrocortisone cream or calamine lotion to reduce itching. Cooling these products in the refrigerator before use may offer extra relief.
-
Take an oral antihistamine such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl) to ease itching and help with sleep, or use a non-drowsy option like loratadine (Claritin).
-
Apply cool, wet compresses for 15 to 30 minutes several times daily.
-
Avoid scratching, keep nails trimmed, and cover itchy areas with a light dressing if needed. Avoid popping blisters and protect healing skin from the sun.
-
Soak the affected area in cool water for about 20 minutes. Adding an oatmeal-based product can help soothe irritation.
-
Protect your hands by rinsing and drying them thoroughly after washing, applying moisturizer regularly, and using gloves suited to your activities—such as cotton-lined plastic gloves for wet work.
Preparing for Your Appointment
You may first visit your primary care provider, who can refer you to a dermatologist if needed. Being prepared helps make the most of your appointment.
What you can do:
-
Write down your symptoms, including when they started and how long they’ve lasted.
-
Avoid suspected triggers and note any new products or substances that come in contact with your skin.
-
List all medications, creams, and supplements you use, including dosages.
-
Prepare questions for your provider.
Questions to Ask Your Health Care Provider
-
What might be causing my symptoms?
-
Are any tests needed to confirm the diagnosis?
-
What treatment options do you recommend?
-
Is this condition likely to go away on its own or become chronic?
-
Can scratching or popping blisters make it worse?
-
What skincare routine should I follow?
-
How can I prevent future flare-ups?
What to Expect from Your Doctor
Your provider may ask questions such as:
-
When did your symptoms begin?
-
Are they constant or do they come and go?
-
Do they improve on weekends or vacations?
-
What seems to make your symptoms better or worse?
-
Have you started using any new soaps, cosmetics, or household products?
-
Do your work or hobbies involve frequent skin contact with potential irritants or chemicals?
Advertisement