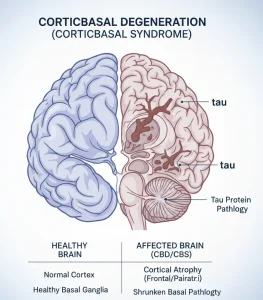
Overview
Diagnosis
A diagnosis of corticobasal degeneration (CBD) — also known as corticobasal syndrome — is based on your symptoms, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. However, because CBD shares symptoms with several other neurological disorders, your healthcare provider must carefully rule out other possible causes.
Other conditions with similar symptoms include:
-
Progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP)
-
Alzheimer’s disease
-
Pick’s disease (a type of frontotemporal dementia)
-
Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
To distinguish between these, your healthcare provider may order several imaging and laboratory tests.
Imaging tests
-
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) or CT (Computed Tomography) scans
-
Used to rule out other brain conditions.
-
These scans may be repeated every few months to detect any progression or new changes in brain structure.
-
-
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scan
-
Helps identify metabolic or functional changes in the brain that may be linked to CBD.
-
Research is ongoing to refine its diagnostic accuracy.
-
Laboratory tests
Your doctor may analyze your blood or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to detect amyloid and tau proteins. The presence and ratio of these proteins can help determine whether Alzheimer’s disease is responsible for your symptoms instead of CBD.
Treatment
Currently, there are no approved treatments that can slow or stop the progression of corticobasal degeneration. However, management focuses on reducing symptoms and improving quality of life.
Medications
-
If Alzheimer’s-related changes are suspected, certain newer medications for Alzheimer’s disease may be considered.
-
Other drugs may be prescribed to help control stiffness, tremors, depression, or sleep problems.
Therapies and supportive care
-
Occupational and physical therapy:
Help maintain mobility and independence, and teach adaptive techniques for daily activities. -
Walking aids and mobility devices:
Reduce the risk of falls and improve balance. -
Speech therapy:
Supports communication and assists with swallowing difficulties. -
Dietitian guidance:
Ensures adequate nutrition and helps reduce the risk of aspiration (inhaling food or liquids into the lungs).
Advertisement