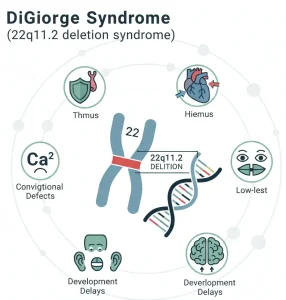
Overview
Diagnosis
A diagnosis of DiGeorge syndrome, also known as 22q11.2 deletion syndrome, is primarily confirmed through a laboratory test that detects a missing section in chromosome 22. Healthcare professionals usually recommend this test when a child shows:
-
A combination of medical issues or developmental delays suggesting 22q11.2 deletion syndrome
-
Heart defects, as certain congenital heart problems are closely associated with this syndrome
In some cases, a child may have clinical signs of the syndrome, but the genetic test may not show a deletion in chromosome 22. In such situations, further evaluations and genetic counseling may be advised.
More Information
Genetic testing plays a central role in confirming DiGeorge syndrome and understanding the extent of the chromosomal deletion. This helps guide treatment plans and long-term care strategies.
Treatment
There is no cure for DiGeorge syndrome (22q11.2 deletion syndrome), but treatments can effectively manage most associated conditions. Medical care focuses on correcting life-threatening issues early, such as heart defects or cleft palate, and providing ongoing support for developmental and behavioral needs.
Treatment and therapy approaches may include:
-
Hypoparathyroidism management: Calcium and vitamin D supplements are commonly prescribed to regulate calcium levels. Additional supplements may be recommended as needed.
-
Heart problems: Many congenital heart defects require early surgical intervention to restore normal blood flow.
-
Limited thymus function: Children with partial thymic function may experience frequent but manageable infections such as colds or ear infections. Standard vaccinations are usually safe, and immune strength often improves with age.
-
Severe thymus dysfunction: When thymic function is severely impaired or absent, the child may face recurrent severe infections. Treatments may involve thymus tissue transplantation, bone marrow cells, or specialized immune cell therapy.
-
Cleft palate: Surgery can usually correct cleft palate and related structural issues of the mouth and lip.
-
Developmental support: Early intervention programs providing speech, occupational, and developmental therapy can help children reach age-appropriate milestones.
-
Mental health care: Children may require psychological support or treatment for conditions such as ADHD, autism spectrum disorder, or depression.
-
Other conditions: Feeding difficulties, growth delays, and hearing or vision problems may also require specific medical management.
Healthcare Team
Because 22q11.2 deletion syndrome affects multiple body systems, a coordinated care approach is essential. The child’s healthcare team may evolve over time depending on ongoing needs.
Key specialists involved in care may include:
-
Pediatrician
-
Geneticist
-
Cardiologist
-
Immunologist
-
ENT specialist (ear, nose, and throat doctor)
-
Infectious disease specialist
-
Endocrinologist
-
Oral and maxillofacial surgeon
-
Cardiovascular surgeon
-
Occupational therapist
-
Speech therapist
-
Developmental therapist
-
Child psychiatrist or psychologist
A multidisciplinary team ensures that each aspect of the child’s health—physical, developmental, and emotional—is addressed comprehensively for improved quality of life.
Advertisement