Overview
Diagnosis
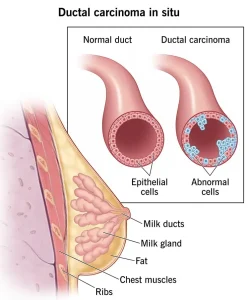
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is often detected during a routine mammogram before symptoms appear. It shows up as clusters of tiny calcifications in the breast ducts. To confirm the diagnosis, your doctor may recommend:
-
Diagnostic mammogram to examine the area more closely
-
Breast ultrasound to evaluate changes in the breast tissue
-
Breast biopsy to analyze cells under a microscope and determine if they are cancerous
DCIS is classified based on its grade, which indicates how abnormal the cells appear and how likely they are to become invasive.
Treatment
Treatment for DCIS aims to remove the affected cells and reduce the risk of recurrence. Common options include:
-
Breast-conserving surgery (lumpectomy) followed by radiation therapy
-
Mastectomy for more extensive cases or when multiple areas are affected
-
Hormone therapy such as tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitors for hormone receptor-positive DCIS
Regular follow-up mammograms and checkups are essential after treatment to monitor for any new changes.
Advertisement