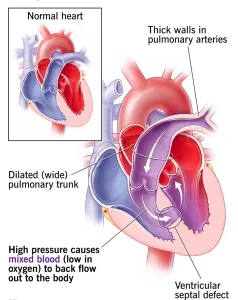
Overview
Diagnosis
Diagnosing Eisenmenger syndrome involves a thorough medical evaluation to understand your symptoms and the structure of your heart and lungs. Your healthcare professional will review your medical history, perform a physical examination, and order several diagnostic tests.
Tests used for diagnosis include:
-
Blood tests: These measure red blood cell count, iron levels, and how well the kidneys and liver are functioning. People with Eisenmenger syndrome often have high red blood cell counts due to low oxygen levels.
-
Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): This painless test records the heart’s electrical activity and can reveal abnormal rhythms or strain on the heart.
-
Chest X-ray: Provides an image of the heart and lungs to identify enlargement or fluid buildup.
-
Echocardiogram: Uses sound waves to create detailed images of the heart, showing how blood moves through the heart chambers and valves.
-
CT scan or MRI of the lungs: Offers detailed images of the lung arteries and surrounding structures. Contrast dye may be used for clearer visualization.
-
Cardiac catheterization: Measures pressure in the heart chambers and arteries, and determines the size and location of any heart defects.
-
Walking test: Assesses how your body responds to light exercise, helping to evaluate how well the heart and lungs are working together.
Treatment
The main goals of Eisenmenger syndrome treatment are to manage symptoms, prevent complications, and improve quality of life. Regular care from a cardiologist experienced in congenital heart disease is essential.
Medications commonly used include:
-
Anti-arrhythmics: Help regulate abnormal heart rhythms.
-
Iron supplements: Prescribed if blood tests show low iron levels, but should only be taken under medical supervision.
-
Aspirin or blood thinners: Recommended in certain cases such as stroke or irregular heartbeats, but used cautiously due to bleeding risks.
-
Bosentan (Tracleer): Helps improve blood flow in the lungs but requires regular liver monitoring.
-
Sildenafil (Revatio, Viagra) or Tadalafil (Cialis, Adcirca): Used to relax blood vessels in the lungs and reduce pulmonary hypertension.
-
Antibiotics: May be prescribed before some dental or surgical procedures to prevent heart infections such as endocarditis.
Surgical and procedural treatments include:
-
Phlebotomy (blood withdrawal): May be performed if red blood cell levels are excessively high and causing symptoms like headaches or blurred vision. It should only be done under expert supervision, with IV fluids to replace lost volume.
-
Heart or lung transplant: Considered in severe cases when other treatments are no longer effective.
Because Eisenmenger syndrome is complex, ongoing follow-up at a specialized heart center is crucial for monitoring changes, adjusting treatment, and preventing complications.
Advertisement