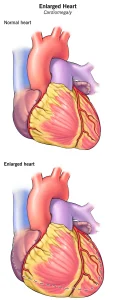
Overview
Diagnosis
To diagnose an enlarged heart (cardiomegaly), your health care provider will typically perform a physical examination and discuss your medical history and symptoms.
Tests commonly used to determine the presence and cause of an enlarged heart include:
-
Blood tests: Help detect conditions that can cause heart enlargement or confirm a heart attack by identifying substances from damaged heart muscle.
-
Chest X-ray: Shows the size and shape of the heart. If the heart appears enlarged, additional tests are performed to confirm.
-
Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): Measures the heart’s electrical activity to detect abnormal rhythms or signs of thickened heart muscle.
-
Echocardiogram: Uses sound waves to create images of the heart’s structure, motion, and blood flow to assess heart function.
-
Exercise or stress tests: Evaluate how the heart responds to physical activity. If unable to exercise, medicines are used to mimic the effects of exercise.
-
Cardiac CT scan or MRI: Creates detailed images of the heart to assess size, structure, and abnormalities.
-
Cardiac catheterization: Involves inserting a thin tube through a blood vessel into the heart to measure pressure, assess blood flow, and possibly collect a tissue sample (biopsy).
Treatment
Treatment for an enlarged heart focuses on addressing the underlying cause and improving heart function.
Medications
-
Diuretics: Help remove excess fluid and sodium, reducing heart workload.
-
Beta blockers, ACE inhibitors, or ARBs: Lower blood pressure and improve heart function.
-
Blood thinners (anticoagulants): Prevent blood clots that may lead to heart attack or stroke.
-
Anti-arrhythmics: Help regulate abnormal heart rhythms.
Surgery and Procedures
If medications alone are insufficient, surgical or device-based treatments may be necessary:
-
Pacemaker: Regulates heart rate and ensures consistent heartbeat.
-
Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD): Monitors heart rhythm and delivers electric shocks if life-threatening arrhythmias occur.
-
Heart valve surgery: Repairs or replaces damaged valves that contribute to heart enlargement.
-
Coronary bypass surgery: Restores blood flow by rerouting around blocked coronary arteries.
-
Left ventricular assist device (LVAD): A mechanical pump that helps the heart circulate blood, often used before or instead of a transplant.
-
Heart transplant: Considered the final option when all other treatments fail, though donor heart availability can be limited.
Advertisement