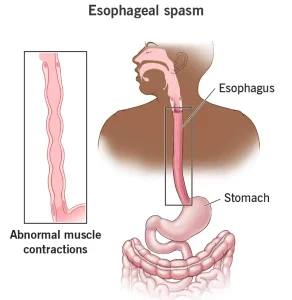
Overview
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of esophageal spasms involves tests that evaluate how the esophagus moves and whether abnormal muscle contractions are occurring.
Upper endoscopy
A healthcare professional uses a thin, flexible tube with a small camera at the tip to view the upper digestive tract. This test helps identify abnormalities in the esophagus and allows tissue collection (biopsy) to rule out other diseases.
X-rays of the upper digestive system (Esophagram)
This test involves swallowing a chalky liquid called barium, which coats the lining of the digestive tract. X-rays are then taken to visualize the esophagus, stomach, and upper intestine. It helps detect abnormal movements or narrowing of the esophagus. Some people may experience loose stools for a day or two after the test.
Esophageal manometry
This test measures the muscle contractions and pressure inside the esophagus when swallowing. It checks how well the muscles coordinate and how effectively the lower esophageal sphincter opens. It’s one of the most accurate ways to diagnose esophageal spasms.
Treatment
Treatment depends on the frequency and severity of esophageal spasms. Mild, occasional spasms may not need medical intervention, while frequent or painful spasms require medication or, rarely, surgery.
1. Lifestyle management
-
Avoid extremely hot or cold foods and beverages.
-
Identify and avoid trigger foods that worsen spasms.
-
Manage stress, as anxiety can worsen muscle contractions.
2. Managing underlying conditions
If spasms are related to GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease) or heartburn, a healthcare professional may prescribe a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) to reduce stomach acid.
Sometimes, low-dose antidepressants such as imipramine may be used to reduce pain sensitivity in the esophagus.
3. Medicines to relax esophageal muscles
-
Peppermint oil: Acts as a natural smooth muscle relaxant.
-
Botox (onabotulinumtoxinA) injections: Temporarily paralyze muscles in the esophagus to reduce spasm intensity.
-
Calcium channel blockers (e.g., diltiazem): Help relax esophageal muscles and reduce pain.
4. Surgical options (for severe cases)
-
Myotomy: A surgical procedure that cuts the lower esophageal muscle to prevent strong contractions. It’s generally reserved for cases that don’t respond to medications.
-
Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (POEM): A minimally invasive version of myotomy performed with an endoscope. It allows the surgeon to access and cut the inner muscle layer of the esophagus through the mouth. POEM is considered when other treatments have failed.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
To reduce discomfort from esophageal spasms:
-
Avoid triggers: Keep a record of foods or drinks that cause symptoms.
-
Adjust food temperature: Eat food that is moderately warm or cool — not too hot or cold.
-
Try peppermint lozenges: Peppermint oil can help relax esophageal muscles and reduce pain.
Preparing for Your Appointment
If you have ongoing symptoms, you may be referred to a gastroenterologist. Here’s how to prepare:
-
Follow any fasting or pre-test instructions.
-
Note your symptoms, their triggers, and duration.
-
Bring a list of all medications, vitamins, or supplements.
-
Include details of other medical conditions or stress factors.
-
Prepare a list of questions for your doctor.
-
Take a friend or family member to help you remember important details from the visit.
Questions to Ask Your Doctor
-
What’s the likely cause of my symptoms?
-
What tests do I need, and how should I prepare for them?
-
Are my symptoms temporary or long-term?
-
What treatment options are available?
-
What foods or drinks should I avoid?
-
How can I manage my other health conditions alongside this one?
What to Expect from Your Doctor
Your healthcare provider may ask:
-
When did your symptoms start, and how severe are they?
-
Are the symptoms constant or occasional?
-
What improves or worsens them?
-
Does physical activity trigger your chest pain?
-
Are your symptoms related to meals or specific foods?
-
Do you experience heartburn, acid taste, or chest pain at night?
-
Have you had difficulty swallowing or changed your diet because of it?
Advertisement