Overview
Diagnosis
A detailed family history is one of the most important steps in diagnosing familial hypercholesterolemia. Healthcare professionals will want to know if any close relatives — such as parents, siblings, aunts, uncles, or grandparents — have experienced high cholesterol levels or early heart disease, particularly during childhood.
During a physical examination, healthcare providers may check for cholesterol deposits on the skin around the hands, elbows, knees, and eyes. The tendons in the heel and hand may appear thickened, and a gray or white ring around the iris, known as corneal arcus, may also be visible.
Cholesterol tests
Blood tests are commonly used to measure cholesterol levels. According to the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, the first cholesterol screening should take place between ages 9 and 11 and be repeated every five years. For families with a history of childhood heart disease, earlier or more frequent screenings may be recommended.
Cholesterol levels are measured differently depending on the region:
-
In the United States, levels are measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL)
-
In Canada and Europe, levels are measured in millimoles per liter (mmol/L)
Typical cholesterol levels in familial hypercholesterolemia include:
-
Adults: LDL cholesterol above 190 mg/dL (4.9 mmol/L) or persistently high levels despite treatment
-
Children: LDL cholesterol above 160 mg/dL (4.1 mmol/L)
-
Severe cases: LDL cholesterol levels above 500 mg/dL (13 mmol/L)
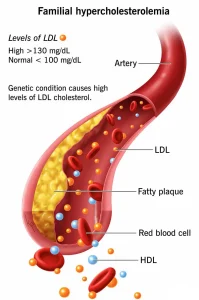
LDL cholesterol, often called the “bad” cholesterol, can accumulate in the artery walls, leading to hardening and narrowing of the arteries. This greatly increases the risk of heart attacks and other cardiovascular complications.
Genetic testing
Genetic testing can confirm a diagnosis of familial hypercholesterolemia, although it is not always necessary for treatment. The test can also identify other family members who may be at risk.
If one parent has the condition, each child has a 50% chance of inheriting it. When both parents carry the altered gene, the result is a rare and more severe form of familial hypercholesterolemia.
Once a diagnosis is confirmed, healthcare professionals usually recommend that all first-degree relatives — including parents, siblings, and children — be tested. Early detection allows for prompt treatment and prevention of heart disease.
Treatment
Treatment for familial hypercholesterolemia focuses on lowering LDL cholesterol levels to reduce the risk of heart attack and related complications. Most people require a combination of medications and lifestyle changes to achieve target cholesterol levels.
Medications
People with familial hypercholesterolemia often need multiple medicines to manage cholesterol effectively. Common options include:
-
Statins such as atorvastatin, rosuvastatin, simvastatin, pravastatin, lovastatin, fluvastatin, and pitavastatin, which block the liver’s production of cholesterol.
-
Ezetimibe, which reduces the amount of cholesterol absorbed from food. It is often prescribed in combination with statins if cholesterol levels remain high.
-
PCSK9 inhibitors such as alirocumab, evolocumab, and inclisiran, which help the liver remove LDL cholesterol from the blood. These are injectable medicines given every few weeks or months.
-
Bempedoic acid, a newer oral medication that reduces LDL cholesterol production in the liver and is generally well tolerated.
Other treatments
For people with severe familial hypercholesterolemia, additional treatments may be necessary. These may include:
-
LDL apheresis, a procedure that filters excess cholesterol from the blood at regular intervals
-
Liver transplant, in rare cases where cholesterol cannot be controlled through medication and other therapies
Ongoing follow-up with a healthcare team is essential to monitor cholesterol levels, adjust treatment, and prevent long-term complications.
Advertisement