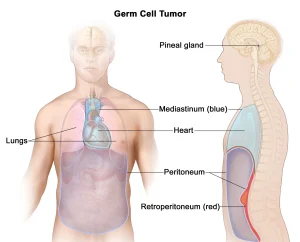
Overview
Diagnosis
Diagnosing germ cell tumors involves a combination of imaging tests, blood tests, and sometimes surgery. These tests help determine the tumor’s location, type, and whether it is cancerous.
Imaging tests
Imaging scans create detailed pictures of the inside of the body, helping identify the size and location of a tumor.
-
Ultrasound is often the first test used, especially for tumors in the ovaries or testicles. It helps determine if a lump appears to be cancerous or noncancerous.
-
CT scan (computerized tomography) and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) may also be used for a more detailed view of the tumor and surrounding tissues.
Blood tests
Blood tests can detect specific proteins made by cancer cells, known as tumor markers.
-
Elevated levels of these proteins don’t always mean cancer is present, but they can give valuable information to guide diagnosis and treatment planning.
Surgery
If imaging and blood tests suggest cancer, surgery may be performed to remove the lump or mass.
-
The removed tissue is sent to a lab for testing to confirm whether it is a germ cell tumor and whether it is cancerous.
Treatment
Treatment for germ cell tumors depends on the type, location, and stage of the tumor. Common treatment options include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.
Surgery
Surgery is often the first treatment for germ cell tumors.
-
The goal is to remove the tumor completely.
-
In cases of testicular cancer, the affected testicle may need to be removed to prevent the spread of cancer.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses powerful drugs to destroy cancer cells.
-
Most chemotherapy medicines are given through a vein, though some may be taken as pills.
-
This treatment may be used alone or combined with surgery or radiation therapy to prevent recurrence.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy targets cancer cells with high-energy beams, such as X-rays or protons.
-
During treatment, you lie on a table while a machine delivers radiation precisely to the tumor site.
-
Radiation therapy is typically used when the cancer cannot be fully removed with surgery or when chemotherapy alone isn’t enough.
Advertisement