Overview
Diagnosis of Hamstring Injuries
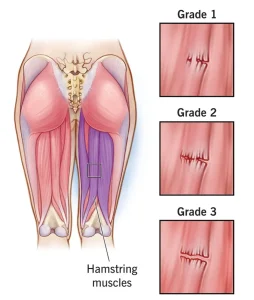
During a physical exam, a healthcare provider checks for swelling and tenderness along the back of the thigh. The location and severity of the pain help determine the extent of the injury.
Movement tests are often performed to:
-
Identify which muscle is injured
-
Determine whether ligaments or tendons are damaged
Imaging Tests
In severe hamstring injuries, the muscle may tear or detach from the pelvis or shinbone. This can sometimes pull a small piece of bone away, known as an avulsion fracture. Imaging tests may include:
-
X-rays to check for avulsion fractures
-
Ultrasound to detect muscle and tendon tears
-
MRI for detailed imaging of soft tissue damage
Early and accurate diagnosis helps guide effective treatment and prevent further injury.
Treatment of Hamstring Injuries
The initial goal of treatment is to reduce pain and swelling. Recommended measures include:
-
Taking a break from strenuous activities
-
Applying ice packs several times a day
-
Using a compression bandage or wearing compression shorts
-
Resting with the leg elevated above heart level if possible
-
Taking over-the-counter pain medicine, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen
Physical Therapy
Once pain and swelling decrease, a healthcare provider or physical therapist can guide gentle hamstring stretching and strengthening exercises. Gradual exercises help restore strength and flexibility and prevent future injury.
Surgery
Most partial hamstring tears heal over time with rest and physical therapy. Surgery may be necessary if:
-
The muscle has pulled away from the pelvis or shinbone
-
There are severe muscle tears that require repair
Surgical intervention is aimed at reattaching the muscle and restoring function.
Advertisement