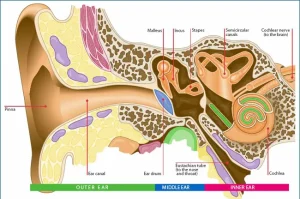
Overview
Diagnosis
Diagnosing hearing loss involves a series of simple and detailed tests to determine the type, cause, and severity of the condition. The evaluation helps healthcare professionals create a personalized treatment plan to improve hearing and quality of life.
Common diagnostic methods include:
-
Physical exam: A healthcare provider examines your ear for causes of hearing loss such as earwax buildup, infection, or structural abnormalities.
-
Screening tests: A basic whisper test may be done by covering one ear at a time while listening to words at varying volumes to assess how well you hear.
-
App-based hearing tests: Mobile applications available on tablets and smartphones can be used for quick, self-administered hearing screenings.
-
Tuning fork tests: These simple tests use a metal tuning fork to produce sound vibrations. They help determine the presence and location of hearing loss within the ear.
-
Audiometer tests: An audiologist performs these advanced tests by delivering tones and words through headphones to each ear. The goal is to measure the quietest sounds you can detect and identify the range of hearing loss.
Treatment
Treatment for hearing loss depends on its cause and severity. Some cases can be corrected with medical treatment or minor procedures, while others require long-term hearing support.
Common treatment options include:
-
Removing earwax: Excess earwax is a frequent cause of temporary hearing loss. It can be safely removed by a healthcare provider using suction or a small curved instrument called a curette.
-
Surgery: Certain types of hearing loss, especially those caused by chronic ear infections or structural issues, may be treated with surgery. In children or adults with repeated ear infections, small tubes may be inserted to help drain fluid from the middle ear.
-
Hearing aids: When hearing loss results from damage to the inner ear, hearing aids can amplify sound and improve hearing clarity. An audiologist can help select and fit the most suitable type of hearing aid based on your needs.
-
Cochlear implants: For severe hearing loss where traditional hearing aids are ineffective, cochlear implants may be recommended. These devices bypass the damaged inner ear structures and directly stimulate the auditory nerve to restore hearing function.
An ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist, together with an audiologist, can help you understand the best treatment options for your specific hearing condition and guide you through rehabilitation and care.
Advertisement