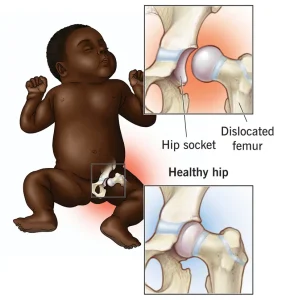
Overview
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of hip dysplasia often begins during infancy. During routine well-baby visits, healthcare professionals check for hip dysplasia by gently moving the baby’s legs into different positions to see how well the hip joint fits together. If there are signs that the hip is not stable or properly aligned, a hip ultrasound may be performed to look for evidence of dysplasia.
In mild cases, hip dysplasia can be difficult to detect and may not cause symptoms until adolescence or early adulthood. When hip pain or instability occurs later in life, imaging tests may be recommended, such as:
-
X-rays to check bone alignment and joint structure
-
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to provide a detailed view of the hip joint and surrounding tissues
Early detection plays a key role in preventing long-term joint damage and improving treatment outcomes.
Treatment
Treatment for hip dysplasia depends on the person’s age and the severity of the condition. The goal is to ensure the hip joint fits properly and functions smoothly.
For infants, a soft brace such as a Pavlik harness is commonly used. This device holds the ball of the hip joint securely in the socket for several months, allowing the socket to form correctly around the ball.
For babies older than six months, the Pavlik harness may not be effective. In such cases:
-
The healthcare provider may reposition the hip bones manually and hold them in place with a spica cast for several months.
-
Surgery may be required if the bones do not align properly through non-surgical methods.
For more severe cases, a periacetabular osteotomy may be performed. This surgical procedure repositions the hip socket in the pelvis so it aligns better with the ball of the joint, improving hip stability and movement.
In adults or older individuals with advanced hip damage or arthritis due to untreated dysplasia, hip replacement surgery may be recommended. This procedure replaces the damaged joint with an artificial one, relieving pain and improving mobility.
Early treatment can prevent complications such as arthritis and chronic pain, ensuring better hip function throughout life.
Advertisement