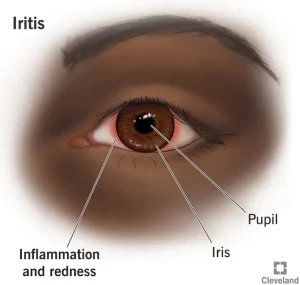
Overview
Diagnosis
Diagnosing iritis begins with a complete eye examination performed by an eye doctor. The evaluation may include:
-
External examination to check pupil reactions, patterns of redness and any discharge
-
Visual acuity testing using an eye chart and other standard vision tests
-
Slit-lamp examination to view internal eye structures for signs of inflammation. Sometimes, pupil dilation drops are used to allow a clearer view inside the eye.
If your eye doctor suspects that another medical condition is causing the iritis, additional tests may be recommended in coordination with your primary care provider. These may include blood tests or X-rays to identify or rule out underlying causes.
Treatment
The main goals of iritis treatment are to relieve pain, reduce inflammation and protect vision. If the iritis is linked to another condition, treating that condition is also an important part of care.
Most treatment plans include:
-
Steroid eyedrops to reduce inflammation
-
Dilating eyedrops to ease pain and prevent complications that affect pupil function
If symptoms don’t improve or become more severe, oral medications may be prescribed. These may include steroids or other anti-inflammatory medicines based on your overall health and how the condition responds to initial treatment.
Advertisement