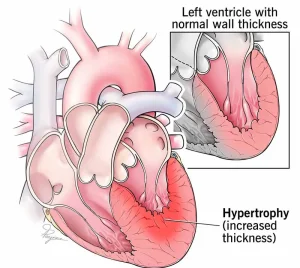
Overview
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of left ventricular hypertrophy begins with a physical examination and a discussion about symptoms and family health history. A healthcare professional checks blood pressure and listens to the heart using a stethoscope.
Tests that may be used to confirm the diagnosis include:
-
Lab tests to assess blood sugar, cholesterol, and liver and kidney function.
-
Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) to measure the heart’s electrical activity and detect patterns that may indicate thickened heart muscle.
-
Echocardiogram to create moving images of the heart, showing blood flow, valve function, and heart muscle thickness.
-
Heart MRI to produce detailed images of the heart structure.
Treatment
Treatment focuses on addressing the underlying cause of left ventricular hypertrophy. This may involve medicines, catheter-based procedures, or surgery. Managing conditions such as high blood pressure and sleep apnea is a key part of preventing further heart muscle thickening.
Medications
Medicines help relieve symptoms, manage risk factors, and prevent complications. Blood pressure-lowering medicines are often used to reduce strain on the heart. Treatment options may include:
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors to widen blood vessels and improve blood flow.
-
Angiotensin II receptor blockers, which offer similar benefits without the persistent cough sometimes caused by ACE inhibitors.
-
Beta blockers to help control heart rate and reduce the force of the heart’s contractions.
-
Calcium channel blockers to relax the heart muscle and widen blood vessels.
-
Water pills, also called diuretics, to remove excess fluid and lower blood pressure.
Surgery or other procedures
When left ventricular hypertrophy is caused by aortic valve stenosis, a catheter procedure or surgery may be required to repair or replace the affected valve.
Procedures may also be needed to manage underlying conditions such as:
-
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, where surgery may be recommended if symptoms of heart failure develop or if a blockage affects the heart’s pumping ability.
-
Amyloidosis, where a stem cell transplant may be considered if other treatments are not effective.
Your healthcare team will work with you to create a treatment plan suited to your specific needs.
Advertisement