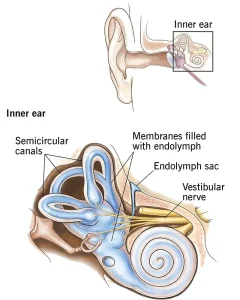
Overview
Diagnosis
A diagnosis of Meniere’s disease begins with a healthcare professional examining you and reviewing your medical history. Key criteria include:
-
Two or more vertigo attacks, each lasting between 20 minutes and 12 hours, or up to 24 hours
-
Hearing loss confirmed by a hearing test
-
Tinnitus or a feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear
Because Meniere’s disease shares symptoms with other conditions, your healthcare provider will also rule out other potential causes.
Hearing assessment
Audiometry is used to test how well you hear different pitches and volumes, as well as your ability to distinguish between similar-sounding words. People with Meniere’s disease often have trouble hearing low frequencies or a combination of high and low frequencies, while midrange frequencies may remain normal.
Balance assessment
Balance typically returns to normal between vertigo attacks, but some ongoing problems may occur. Tests to assess inner ear function include:
-
Electronystagmogram or videonystagmography (ENG or VNG), including a caloric test using warm or cold air or water in the ear
-
Rotary-chair testing, where a computer-controlled chair spins side to side to measure inner ear activity
-
Vestibular evoked myogenic potentials (VEMP) testing to evaluate muscle reactions to sound
-
Computerized dynamic posturography (CDP) to identify which parts of the balance system may cause issues
-
Video head impulse test (vHIT) to assess eye and inner ear coordination
-
Electrocochleography (ECoG) to detect fluid buildup in the inner ear
Tests to rule out other conditions
Lab tests, imaging scans like CT or MRI, and other evaluations may be used to exclude other causes of vertigo and hearing problems, such as brain tumors or multiple sclerosis.
Treatment
There is no cure for Meniere’s disease, but treatments can reduce the severity and duration of vertigo attacks. Permanent hearing loss currently cannot be reversed.
Medicines for vertigo
During vertigo attacks, your healthcare provider may prescribe:
-
Motion sickness medicines such as meclizine or diazepam to reduce spinning sensations and control nausea
-
Anti-nausea medicines like promethazine
-
Diuretics and betahistine to improve vertigo, lower inner ear fluid, and enhance blood flow
Long-term management may include medications to reduce fluid retention and dietary adjustments, such as limiting salt intake.
Noninvasive therapies and procedures
-
Vestibular rehabilitation therapy to improve balance between attacks
-
Hearing aids to improve hearing in the affected ear
Middle ear injections
In-office injections may include:
-
Gentamicin, an antibiotic that damages the affected inner ear to control vertigo, with some risk of further hearing loss
-
Steroids such as dexamethasone to reduce vertigo symptoms, with a lower risk of hearing loss
Surgery
Surgery may be considered if vertigo attacks are severe and other treatments fail:
-
Endolymphatic sac surgery to relieve inner ear fluid pressure
-
Labyrinthectomy, which removes inner ear structures causing vertigo, resulting in total hearing loss in that ear
-
Vestibular nerve section, which cuts the nerve transmitting balance signals to the brain, often preserving hearing in the affected ear
Some surgical procedures require general anesthesia and an overnight hospital stay.
Advertisement