Overview
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of metabolic syndrome is based on a combination of medical history, family medical history, a physical examination, and results from blood pressure measurements and blood tests. These evaluations help assess risk factors that often occur together and increase the chances of heart disease, stroke and diabetes.
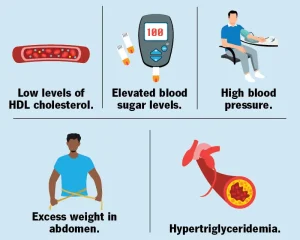
According to the National Institutes of Health, metabolic syndrome is diagnosed when a person has three or more of the following conditions, or is taking medication to manage these conditions:
-
Large waist
A waist measurement of at least 35 inches for women or 40 inches for men. -
High triglyceride level
Triglycerides of 150 milligrams per deciliter or higher. -
Low HDL cholesterol
HDL cholesterol levels below 40 milligrams per deciliter in men or below 50 milligrams per deciliter in women. -
High blood pressure
A blood pressure reading of 130/80 millimeters of mercury or higher. -
High fasting blood sugar
A fasting blood glucose level of 100 milligrams per deciliter or higher.
Treatment
Treatment for metabolic syndrome usually begins with lifestyle changes. Improving daily habits can significantly reduce risk factors and may prevent the need for medication.
Lifestyle changes typically focus on healthier eating patterns, regular physical activity and weight management. These changes help improve blood pressure, cholesterol levels and blood sugar control.
If lifestyle changes alone are not effective, medications may be recommended. Medicines can help manage high blood pressure, abnormal cholesterol levels and elevated blood sugar, reducing the risk of long-term complications.
Advertisement