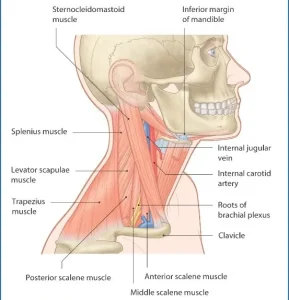
Overview
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of neck pain begins with a medical history and physical exam. Your healthcare provider will check for tenderness, numbness, muscle weakness, and assess your range of motion, including forward, backward, and side-to-side movements of the head.
Imaging tests
Imaging can help identify the cause of neck pain, including:
• X-rays: Reveal areas where nerves or the spinal cord may be pinched by bone spurs or other changes
• CT scan: Combines X-ray images from different angles to create detailed cross-sectional views of the neck
• MRI: Uses radio waves and a magnetic field to create detailed images of bones and soft tissues, including discs, spinal cord, and nerves
Imaging results should be interpreted alongside a careful history and physical exam, as structural changes may exist without causing symptoms.
Other tests
• Electromyography (EMG): Measures nerve conduction speed by inserting fine needles into muscles to detect nerve-related pain
• Blood tests: Can identify inflammation or infections that may contribute to neck pain
Treatment
Mild to moderate neck pain often improves within two to three weeks with self-care, heat, and over-the-counter pain relief.
Medications
Pain relievers may include:
• Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen or naproxen
• Acetaminophen for pain relief
• Prescription NSAIDs or muscle relaxants if over-the-counter options are insufficient
Therapy
• Physical therapy: Teaches proper posture, alignment, and neck-strengthening exercises; may include heat or ice
• Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS): Electrodes deliver small electrical impulses to reduce pain, though evidence of effectiveness is limited
• Soft neck collar: Provides temporary support; avoid using more than three hours at a time or for longer than 1–2 weeks
Surgical and other procedures
• Steroid injections: Administered near nerve roots, spinal joints, or muscles to reduce pain; may include numbing medications
• Surgery: Rarely required, but may be an option for relieving compression of nerve roots or the spinal cord
Advertisement