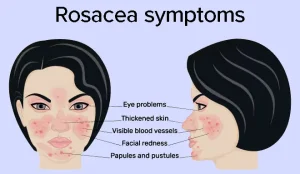
Overview
Diagnosis
Ocular rosacea is often diagnosed based on your symptoms, medical history, and a physical examination of your eyes and eyelids. Because its symptoms can resemble other eye conditions, such as blepharitis or dry eye syndrome, diagnosis can sometimes be challenging.
Your eye doctor may:
-
Examine your eyes using a slit lamp microscope to check for redness, swelling, and visible blood vessels.
-
Inspect your eyelids for inflammation or blocked oil glands.
-
Ask about facial skin symptoms such as redness, flushing, or acne-like bumps that may suggest rosacea.
In some cases, your healthcare provider may work with a dermatologist to confirm whether your skin and eye symptoms are related to rosacea.
Treatment
While ocular rosacea has no cure, treatment focuses on controlling symptoms, reducing inflammation, and preventing complications such as corneal damage. Managing the condition early can help protect your vision and improve comfort.
Home and self-care measures:
-
Apply warm compresses to your eyelids several times a day to help unclog oil glands.
-
Clean your eyelids gently with diluted baby shampoo or a mild eyelid cleanser to remove debris.
-
Avoid touching or rubbing your eyes, which can worsen irritation.
-
Use artificial tears or lubricating eye drops to relieve dryness and burning.
-
Protect your eyes from wind and sunlight by wearing sunglasses outdoors.
Medical treatments:
-
Antibiotics: Your doctor may prescribe oral antibiotics such as doxycycline, tetracycline, or minocycline to reduce inflammation and improve oil gland function. In some cases, antibiotic eye drops or ointments may be used.
-
Anti-inflammatory eye drops: Steroid or cyclosporine drops may be recommended for short-term use to control inflammation.
-
Artificial tears: Prescription lubricants or gels can help manage dryness and irritation.
-
Management of facial rosacea: Treating facial rosacea with topical or oral medications may also help reduce ocular symptoms.
Lifestyle and prevention tips:
-
Identify and avoid triggers that worsen rosacea, such as spicy foods, alcohol, caffeine, extreme temperatures, or stress.
-
Maintain good eyelid hygiene as part of your daily routine.
-
Follow your doctor’s instructions carefully and attend regular follow-up appointments to monitor eye health.
With consistent care and treatment, most people with ocular rosacea can effectively manage their symptoms and prevent long-term eye complications.
Advertisement