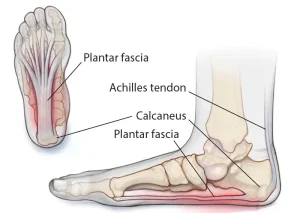
Overview
Diagnosis
Plantar fasciitis is usually diagnosed based on your medical history and a physical examination. During the exam, your healthcare professional will check for areas of tenderness in your foot. The location of your pain can help identify the cause.
Imaging tests are not commonly required, but your healthcare professional might suggest them to rule out other conditions, such as a stress fracture. Possible imaging tests include:
• X-ray
• MRI
Sometimes an X-ray may reveal a bone spur on the heel. However, many people with heel bone spurs do not experience pain, and spurs are not always the cause of plantar fasciitis.
Treatment
Most cases of plantar fasciitis improve within several months using conservative treatments such as icing, stretching, and modifying activities that worsen the pain.
Medicines
Over-the-counter pain relievers, including ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB) or naproxen sodium (Aleve), can help reduce pain and inflammation.
Therapies
Several therapies may help relieve symptoms:
• Physical therapy. Exercises to stretch the plantar fascia and Achilles tendon, strengthen lower leg muscles, and athletic taping to support the foot.
• Night splints. Devices that hold the plantar fascia and Achilles tendon in a lengthened position overnight.
• Orthotics. Off-the-shelf or custom-fitted arch supports to distribute pressure on the feet more evenly.
• Walking boot, canes, or crutches. Short-term use may reduce weight-bearing and movement on the foot.
Surgical or other procedures
If conservative treatments fail after several months, additional options may include:
• Injections. Steroid injections for temporary pain relief or platelet-rich plasma injections to promote tissue healing.
• Extracorporeal shock wave therapy. Sound waves targeted at the heel to stimulate healing.
• Ultrasonic tissue repair. A minimally invasive procedure that uses ultrasound-guided vibration to remove damaged fascia tissue.
• Surgery. Rarely, surgery to detach the plantar fascia from the heel bone may be needed for severe cases that do not respond to other treatments. This can be done through a small incision or open surgery under local anesthesia.
Advertisement